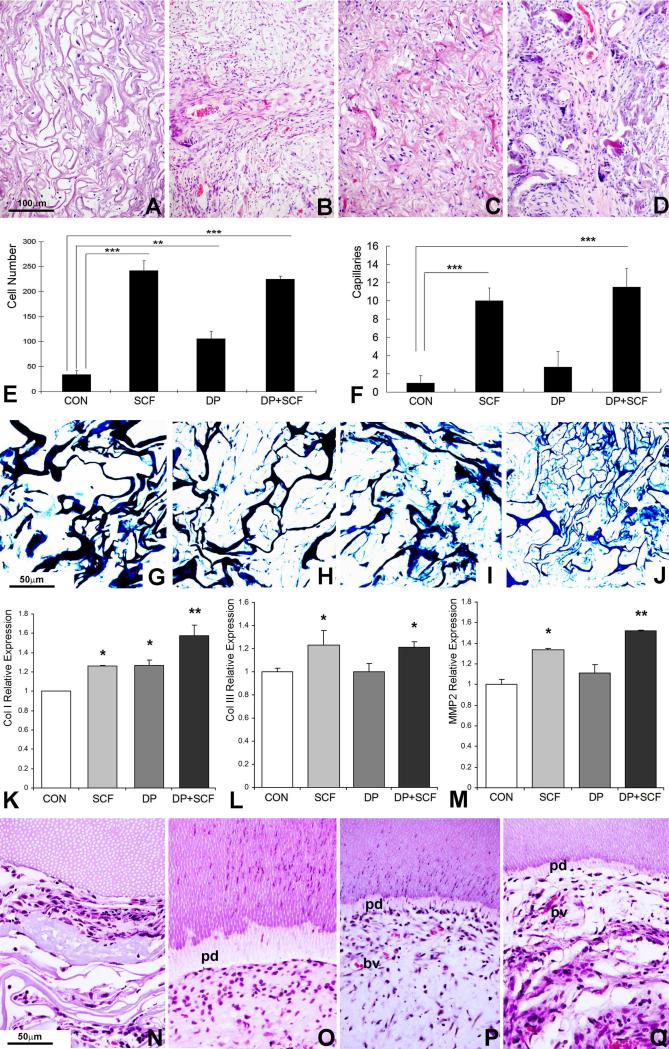
Figure 5. Effect of SCF on cell homing and dental pulp regeneration in vivo.
Collagen sponges were treated either with SCF or seeded with DP cells or both, and subcutaneously implanted into nude mice for 1 or 4 weeks. (A-D) H & E staining of collagen sponge implants subjected to four different types of treatment: collagen sponge control (A), collagen sponge treated with SCF (B), collagen sponge seeded with DP cells (C) and collagen sponge seeded with DP cells and treated with SCF (D). Note the formation of pulp-like tissues in the two groups in which the scaffold was seeded with pulp progenitors (C,D versus A,B). (E) Cell number per field averaging three different implants per group. Four treatment groups were compared: collagen implant without cells (Con), collagen implant treated with SCF but without cells (SCF), collagen implant with dental pulp progenitors (DP), and collagen implant with dental pulp progenitors and SCF treatment (DP+SCF). (F) Number of capillaries per field averaging three different implants and using the same four treatment groups described in (E). (G-J) Visualization of collagen fibers in subcutaneous implants using methyl blue staining comparing four groups of treatment: collagen sponge control (G), collagen sponge treated with SCF (H), collagen sponge seeded with DP cells (I) and collagen sponge seeded with DP cells and treated with SCF (J). Note the degradation of thick collagen fibers and replacement with thin fibers forming smaller subunits in the SCF treated groups (H,J versus G,I). (K-M) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of matrix remodeling related gene expression in subcutaneous implants subjected to dental pulp progenitor preseeding and SCF treatment (groups as in E,F). Levels of gene expression of Collagen I (K), Collagen III (L), and MMP2 (M) were calculated relative to control group gene expression levels. (N-Q) Micrographs of decalcified and H&E stained sections from co-implanted tooth slice/pulp regenerates. Tooth slice/pulp regenerates were implanted subcutaneously for four weeks. The four groups were collagen sponge alone (N), collagen sponge plus SCF (O), collagen sponge plus dental pulp stem cells (P), and sponge plus SCF plus dental pulp stem cells (Q). Note a new layer of predentin (pd) in the groups treated either with SCF or stem cells or both (O-Q). The two groups treated with dental pulp stem cells featured small capillaries (bv)(P,Q). Only the dental pulp stem cell groups featured odontoblast like cells oriented perpendicular to the dentin surface (P,Q), while the group treated with SCF alone displayed oval-shaped round cells parallel to the dentin surface (O). * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p <0.001.