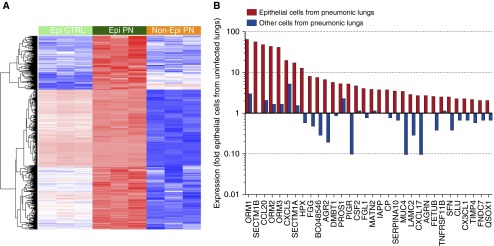
Figure 1.
Genes induced by pneumonia selectively in epithelial cells. (A) Heatmap of 1,166 genes with significantly higher expression in epithelial cells from pneumonic lung compared with both other groups during pneumonia (false discovery rate [FDR] q < 0.05). Epi CTRL, epithelial cells from uninfected mouse lungs; Epi PN, epithelial cells from pneumonic mouse lungs; Non-Epi PN, nonepithelial cells from pneumonic mouse lungs (n = 3 mice per group, each column from an independent mouse). Red intensity represents the degree of higher level of expression, and blue intensity the degree of lower level of expression. (B) To identify secreted proteins induced especially in epithelial cells owing to pneumonia, the genes with significant (FDR q < 0.05) and strong (>twofold) up-regulation in epithelial cells from mice with pneumonia compared with both other groups (epithelial cells from uninfected mice and nonepithelial cells from pneumonic mice) were probed using Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery Bioinformatics. A total of 32 genes were identified as secreted proteins based on the SP_PIR_Secretion annotation. Expression of each transcript in the indicated cell population is shown normalized to the relative expression of that transcript in epithelial cells sorted from uninfected mouse lungs.