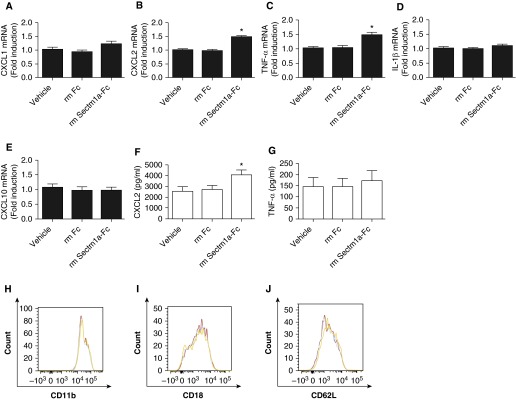
Figure 6.
Sectm1a promotes chemokine (C-X-C) motif ligand (CXCL) 2 production by neutrophils from the pneumonic lung. C57BL/6 mice were infected with S. pneumoniae serotype 19F, and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid was collected 20 hours after infection, from which neutrophils were isolated. Isolated neutrophils were cultured and stimulated with vehicle, Fc (39 μg/ml, stoichiometrically matched to recombinant mouse Sectm1a-Fc), or Sectm1a-Fc (60 μg/ml) for 2 hours (A–E), 8 hours (F and G), or 4 hours (H–J). (A–E) qRT-PCR was performed on total cellular RNA to determine the gene expressions of CXCL1, CXCL2, TNF-α, IL1-β, and CXCL10. Values represent fold induction relative to vehicle group and were expressed as means (±SEM). Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test (n = 9 per group). *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. (F and G) CXCL2 and TNF-α levels were measured by ELISA from culture supernatants of neutrophils. Values represent fold induction relative to vehicle and were expressed as means (±SEM). Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post hoc test (n = 9 per group). *P < 0.05 versus vehicle. (H–J) After stimulation, neutrophils were washed and stained with anti-mouse CD45, Ly6G, CD11b, CD18, and CD62L antibodies. The expression of surface markers, including CD11b, CD18, and CD62L, was determined in each group using flow cytometry. Cells represented in red, blue, or orange histograms reflect those stimulated with vehicle, Fc, or Sectm1a-Fc, respectively. Results are representative of four samples.