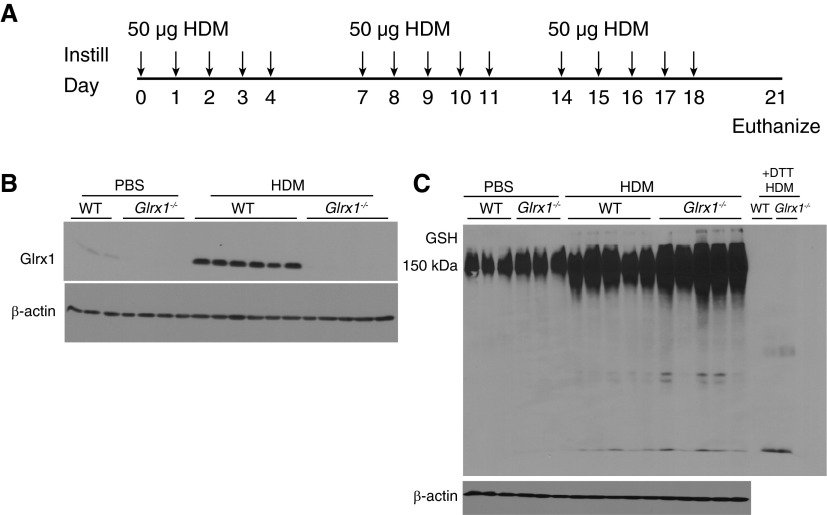
Figure 1.
Evaluation of protein S-glutathionylation (PSSG) and glutaredoxin-1 (Glrx1) expression in the whole lung after house dust mite (HDM) challenge. (A) Schematic depicting repeated intranasal instillation of 50 µg of HDM or PBS for the vehicle control and death on Day 21, 72 hours after the final challenge. (B) Immunoblot for Glrx1 in homogenized lung tissue; β-actin is shown as a loading control. Immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments; wild-type (WT) PBS (n = 3), Glrx1−/− PBS (n = 4), WT HDM (n = 6), and Glrx1−/− HDM (n = 5). (C) Immunoblot for total glutathione (GSH) in homogenized lung tissue. Lung tissue homogenates were electophoresed under nonreducing conditions, transferred into nitrocellulose, and probed with an anti-GSH antibody. +1,4-Dithiothreitol (DTT), representative samples from WT or Glrx1−/− mice exposed to HDM incubated with DTT before electrophoresis, to reduce PSSG as a reagent control; β-actin is shown as a loading control. Immunoblots are representative of three independent experiments; WT PBS (n = 3), Glrx1−/− PBS (n = 3), WT HDM (n = 5), and Glrx1−/− HDM (n = 5).