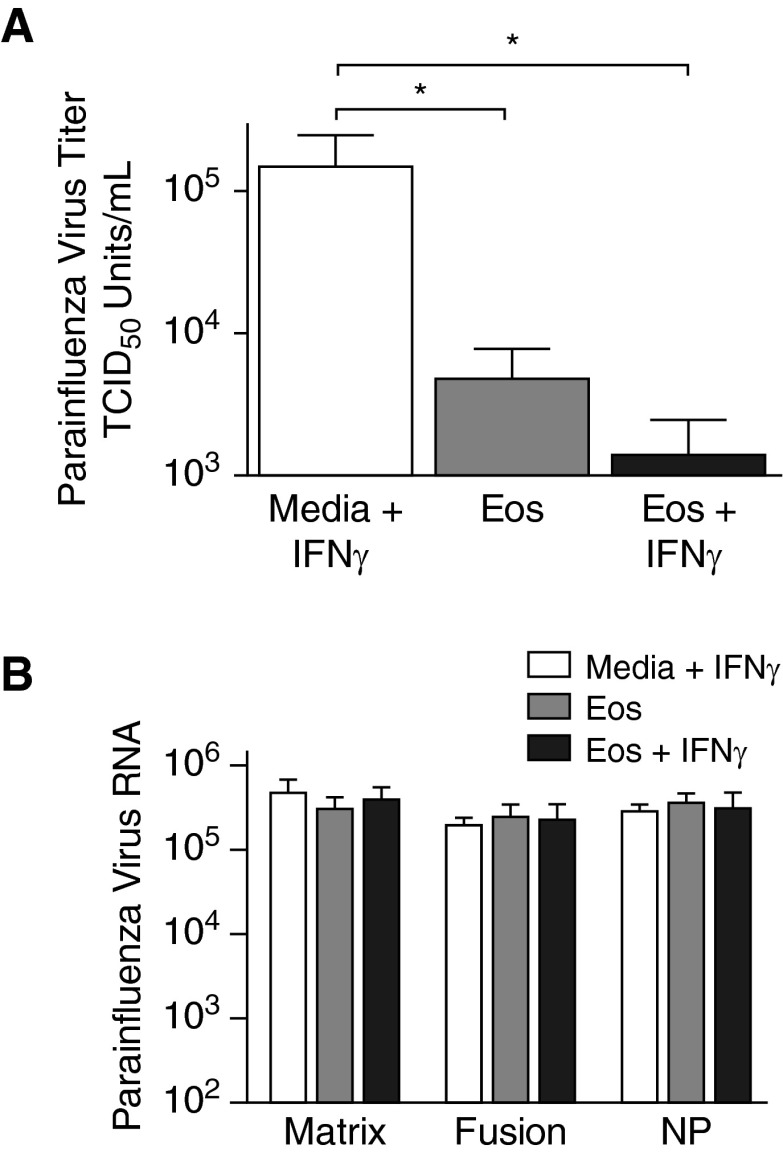
Figure 5.
Eosinophils’ antiviral activity against parainfluenza does not involve granule RNases. Human eosinophils were isolated from peripheral blood and infected with parainfluenza virus. (A) Viral infectivity was assessed 2 hours after inoculation by hemadsorption assay and expressed as viral TCID50 U/ml. Parainfluenza infectivity was nearly undetectable in the supernatants of cultured eosinophils (Eos) and eosinophils pretreated with IFNγ (Eos + IFNγ) compared with parainfluenza virus cultured in media without eosinophils (Media + IFNγ). (B) RNA encoding parainfluenza virus structural proteins, matrix, fusion, and nucleoprotein (NP) was quantified in eosinophil supernatants by real-time RT-PCR 2 hours after inoculation. No differences were detected between any of the three genes, suggesting that the reduction in parainfluenza infectivity was not due to viral RNA degradation by eosinophil granule RNases (n = 4–7). *P < 0.05. Data are presented as means (±SEM).