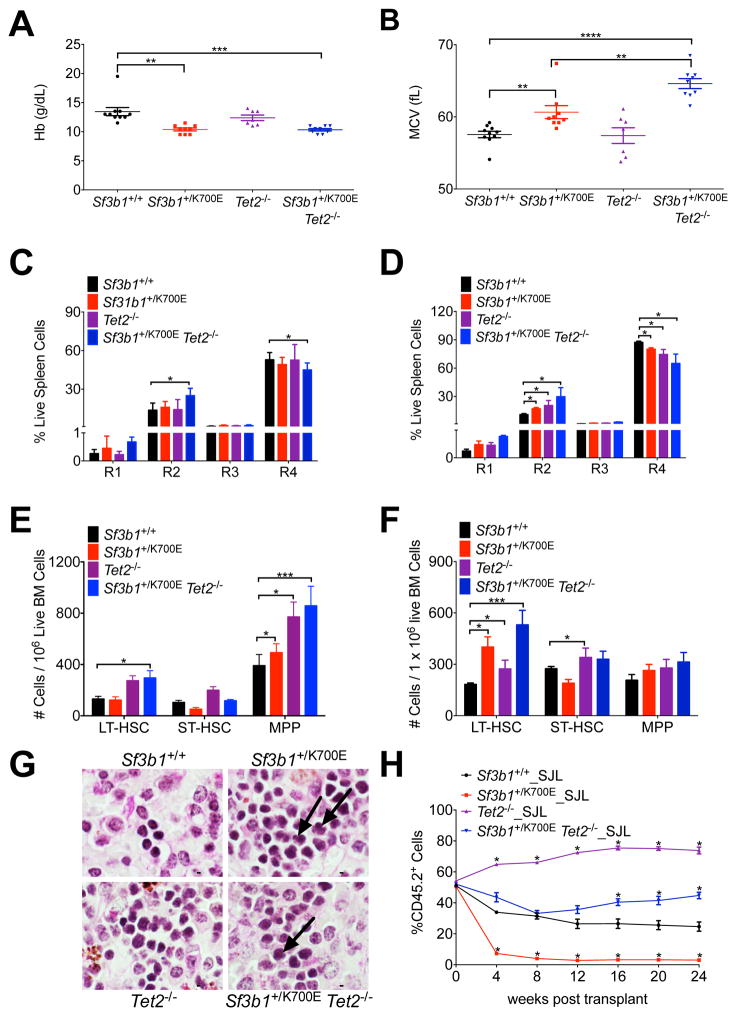
Figure 5. The combination of the Sf3b1K700E mutation and Tet2 deletion causes an earlier onset of MDS characteristics and rescues the competitive disadvantage of Sf3b1+/K700E stem cells.
(A–B) Peripheral blood Hb (A) and MCV (B) from Sf3b1+/+, Sf3b1+/K700E, Tet2−/−, and Sf3b1+/K700E Tet2−/− mice 45 weeks post-pIpC (n = 7–10 mice per group). (C–D) Analysis of terminal erythroid maturation in the spleens of Sf3b1+/+, Sf3b1+/K700E, Tet2−/−, and Sf3b1+/K700E Tet2−/− mice 12 (C) and 45 (D) weeks post-pIpC (n = 7–10 mice per group). (E–F) Number of LT-HSCs, ST-HSCs, and MPPs in the bone marrow of Sf3b1+/+, Sf3b1+/K700E, Tet2−/− and Sf3b1+/K700E Tet2−/− mice 12 (E) and 45 (F) weeks post-pIpC (n = 7–10 mice per group). (G) Periodic acid-Schiff stained spleens from Sf3b1+/+, Sf3b1+/K700E, Tet2−/−, and Sf3b1+/K700E Tet2−/− mice, 45 weeks post-pIpC. Arrows indicate dysplastic erythroid precursors. Scale bar indicates 5 μM. (H) Percentage of CD45.2 donor chimerism in the peripheral blood 4 to 24 weeks after competitive repopulation assay with 1:1 unfractionated bone marrow from Sf3b1+/+, Sf3b1+/K700E, Tet2−/−, or Sf3b1+/K700E Tet2−/− CD45.2+ mice and CD45.1+ B6.SJL mice transplanted into lethally irradiated B6.SJL recipients (n = 5 mice per group). CD45.2 chimerism of the input bone marrow was measured at time 0 (n = 1 sample per group). Data presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001. See also Figure S5.