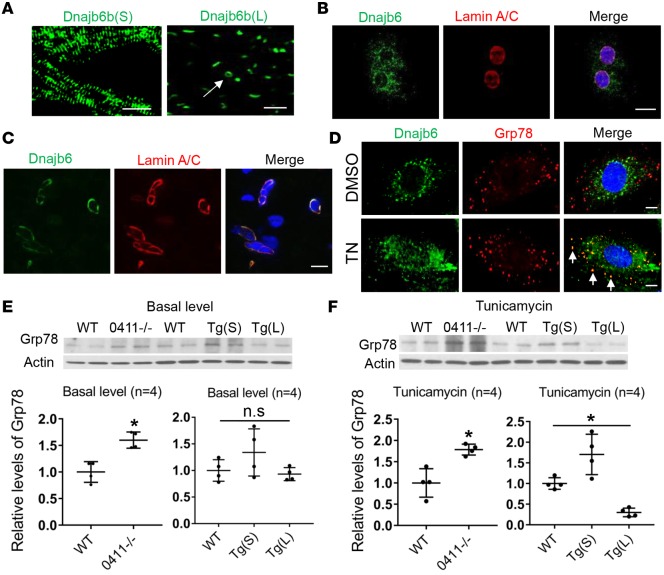
Figure 3. Dnajb6b(L) localizes to the nuclear envelope and functions as an ER stress inhibitor.
(A) EGFP reporter imaged from Tg(cmlc2:dnajb6b(S)-EGFP) fish heart (left) indicated sarcomeric localization of Dnajb6b(S). EGFP reporter from the Tg(cmlc2:dnajb6b(L)-EGFP) fish heart (right) indicated a primary nuclear localization and an occasional perinuclear localization (arrow) for the Dnajb6b(L). Scale bars: 10 μm. (B and C) Costaining of anti-Dnajb6 with the nuclear envelope protein anti-Lamin A/C antibodies in the HL-1 cell line (B) and in sections of WT C57BL/6 mice heart (C) merged with DAPI (blue), indicating Dnajb6 localization to the nuclear envelope. Scale bar: 10 μm. (D) Costaining of anti-Dnajb6 with the ER-resident protein glucose-regulated protein (Grp78) antibody indicated a partial colocalization (arrows) in the ER of the H9c2 cell line after tunicamycin (TN) treatment (1 μg/mL for 24 hours). Scale bar: 10 μm. (E and F) Western blot (upper) and quantification (lower) analysis of Grp78, an ER stress marker, in the GBT0411–/– mutant, Tg(cmlc2:dnajb6b(S)-EGFP), Tg(cmlc2:dnajb6b(L)-EGFP), and WT sibling fish hearts at both basal level (E) and upon TN treatment (F). Values in E and F are expressed relative to WT controls. Data represent mean ±SEM; 1-way ANOVA comparisons, *P < 0.05.