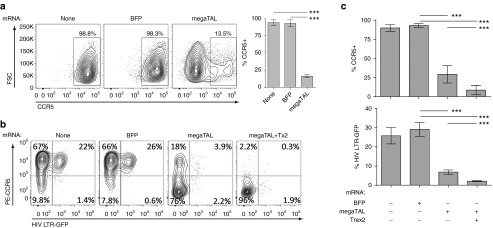
Figure 2.
megaTAL efficiently disrupts CCR5 in Ghost Hi-5 cells and protects against HIV in vitro. (a) Representative flow cytometry data (left) and statistical representations (bar graphs; right) of CCR5 surface expression in an untransfected sample or samples electroporated with either blue fluorescent protein or CCR5 megaTAL mRNA (n = 3). (b) Representative flow cytometry data showing surface CCR5 expression versus intracellular GFP expression. Phycoerythrin-labeled anti-CCR5 antibody was used to assess CCR5 surface expression (vertical axis), and HIV infection was tracked by HIV-2 LTR-driven GFP expression (horizontal axis) in Ghost Hi-5 cells infected 1 week following mRNA transfection using the CCR5-tropic virus HIV BaL. HIV infection preferentially occurs in CCR5+ cell populations (TR). (c) Statistical representations (n = 6) of Ghost Hi-5 cells shown in b, showing CCR5 surface staining (upper panel) and GFP expression (lower panel). All data represent mean ± SD. P values calculated using Student's t-test. Results of statistical analyses in this and subsequent figures as follows: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n.s. = not significant.