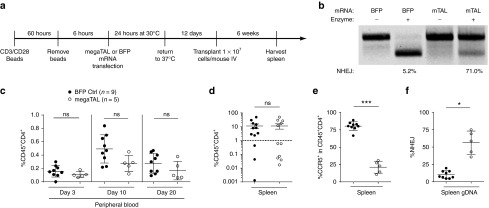
Figure 4.
Primary CD4+ cells modified by CCR5 megaTAL engraft in the immunodeficient NSG murine model and show stable modification of CCR5. (a) Timeline representing workflow for NSG mouse experiment. (b) Re-cleavage assay (RCA) of input cells shows 71% modification at CCR5 in cells treated with CCR5 megaTAL mRNA and 5.2% background modification in cells transfected with blue fluorescent protein. (c) Mice were bled on days 3, 10, and 20 post-transplant. Surface staining of hCD45 and hCD4 was used to track engraftment in peripheral blood over time. (d) Six weeks post-transplant, mice were killed and spleens were harvested. Splenic engraftment of human T cells was tracked through surface staining of hCD45 and hCD4. (e,f) Samples with >1% splenic T engraftment were subsequently analyzed for: (e) surface expression of CCR5 by flow cytometry and (f) molecular quantification of CCR5 disruption by RCA analysis of genomic DNA (gDNA).