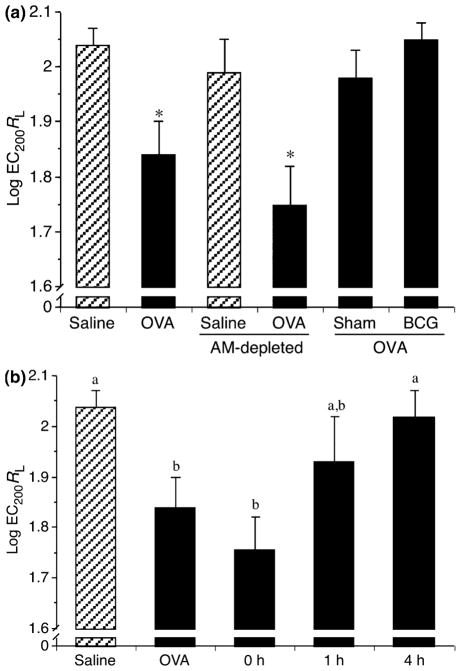
Fig. 5.
AHR of control rats, AM-depleted rats, and repleted with ex vivo cultured AM (Sham or BCG treated). AHR was measured following methacholine challenge and EC200 values were calculated. These values were transformed to log to best fit the natural exponential phenomenon. Hatched and closed bars represent saline and OVA challenge, respectively. (a) AMs were treated for 18 h before being instillated into AM-depleted rats. As expected, OVA challenge significantly increased AHR (*P<0.05) compared with saline in the control group and AM-depleted rats, whereas Sham- and BCG-treated AM abrogated AHR. Means ± SEM of 10 experiments. (b) AMs were cultured for 0, 1, or 4 h before being instillated into AM-depleted rats. Allergen challenge (OVA) significantly increased AHR, whereas transfer of 4 h cultured AMs abrogated AHR. Shorter treatment periods showed variable data (a and b are different, P≤0.05). Means ± SEM of three to four experiments. OVA, ovalbumin; AM, alveolar macrophage; AHR, airway hyperresponsiveness; BCG, Bacillus Calmette-Guerin.