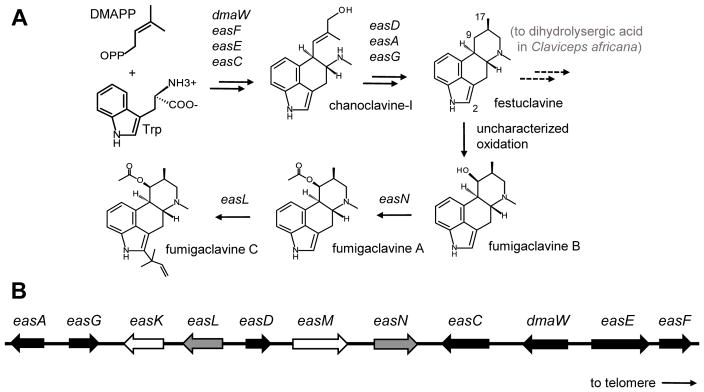
Fig 1.
Ergot alkaloid pathway and gene cluster in N. fumigata. (A) Key intermediates and products in the ergot alkaloid pathway of N. fumigata. Genes controlling steps are indicated between alkaloids. The positions of carbon molecules mentioned by number in the text are labeled in festuclavine. (B) Ergot alkaloid gene cluster of N. fumigata [redrawn from Unsöld and Li (2005); Coyle and Panaccione (2005)]. Black arrows represent genes conserved among ergot alkaloid producers in the Trichocomaceae and Clavicipitaceae and required to assemble the first tetracyclic intermediate. Arrows shaded gray represent genes with established roles in the fumigaclavine branch of the pathway and found only in ergot alkaloid clusters of certain Trichocomaceae. White arrows represent P450 monooxygenase genes that have not been functionally analyzed. The relative position of the telomere on the long arm of chromosome 2 is indicated