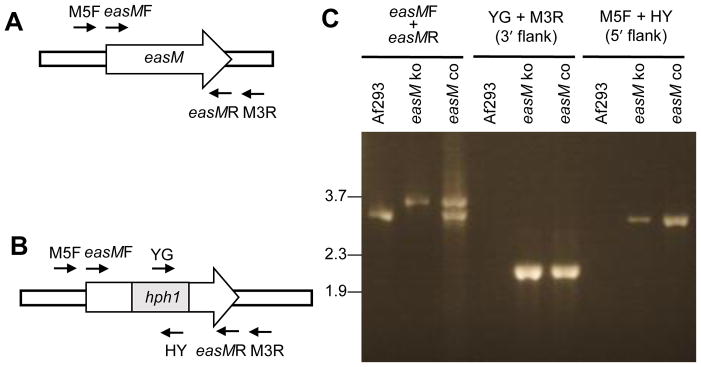
Fig 2.
Knockout of easM in N. fumigata. Schematic representation of easM locus in N. fumigata Af293 before (A) and after (B) gene knock out. Relative positions of PCR primers are indicated. Refer to Table 1 for information on primers and PCR products. hph1 represent the hygromycin phosphotransferase gene replacing part of easM. Primers M5F and M3R anneal to regions of the N. fumigata chromosome that flank the recombination site, thus when paired with primers that anneal to hph1 prime amplification only from strains in which the knockout construct has integrated at easM. (C) PCR products of N. fumigatus Af293 wild type, easM knockout (easM ko), and easM complemented (easM co) strains primed with the indicated oligonucleotides. Relative mobility of relevant fragments of BstEII-digested bacteriophage λ DNA is indicated to the left of photograph