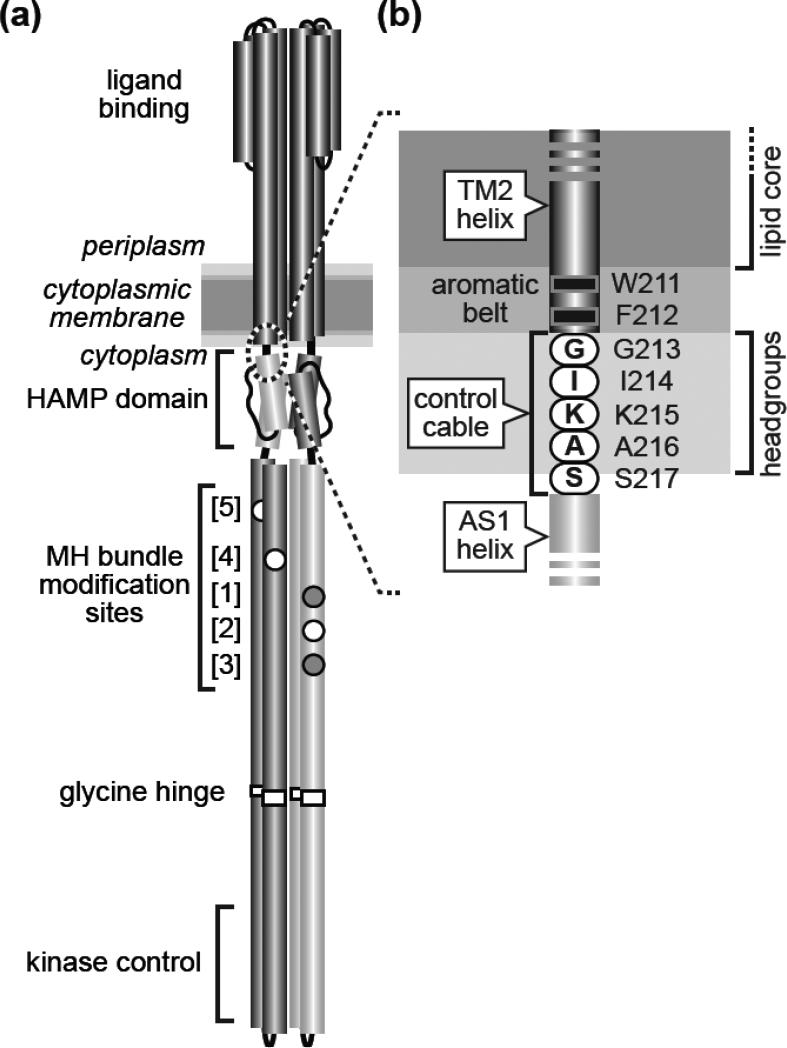
Fig. 1. Tsr structural features and transmembrane signaling models.
(a) The Tsr homodimer [1]. Cylindrical segments represent α-helices, drawn approximately to scale. Each Tsr subunit contains five adaptation sites within a methylation-helix (MH) bundle. Sites 2, 4, and 5 (white circles) are translated as glutamic acid residues, the substrate for CheR methylation. Sites 1 and 3 (gray circles) are translated as glutamine residues that can be deamidated to glutamic acid residues by CheB, making them competent for subsequent methylation. This study focuses on the Tsr region at the membrane-cytoplasm interface (dashed circle), enlarged in (b).
(b) The Tsr control cable. Detail of the dashed region in (a). The aromatic residues at the C-terminus of the TM2 transmembrane helix and the following control cable residues are shown at their probable positions relative to the hydrophobic (lipid core) and polar (headgroup) membrane regions [14].