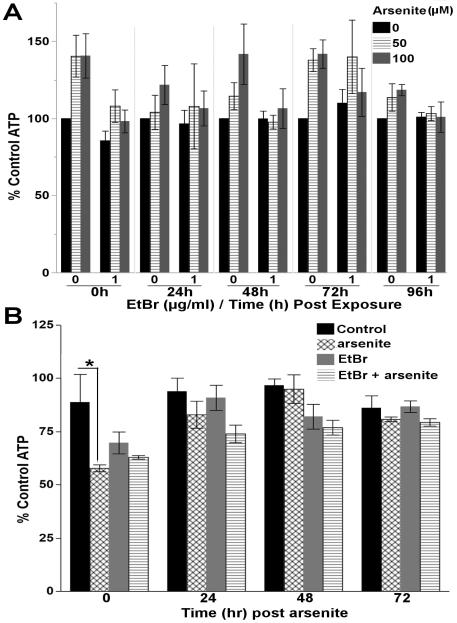
Figure 7. Reduced mtDNA content sensitizes C. elegans to arsenite.
(A) A persistent trend in increased steady-state ATP levels was observed following a 48h liquid exposure to arsenite, while reducing mtDNA content with EtBr prevented the observed trend (3 way ANOVA, EtBr*arsenite interaction (p=0.048)). P-values for all effect and interaction terms are shown in Supplemental File 1. Relative luminescence values are shown in Supplemental Figure 9. (B) Inhibition of glycolysis with 2-deoxy-D-glucose significantly reduces steady-state ATP levels in nematodes treated with 100μM arsenite immediately after (T=0) arsenite exposure demonstrating the induction of glycolysis (one way ANOVA, p=0.045). However, this effect was not observed in nematodes treated with 1.0μg/ml EtBr or co-treated with EtBr and arsenite, nor is the induction of glycolysis persistent (p>0.05 for one way ANOVAs 24, 48, 72h post arsenite). Asterisk denotes statistical significance (p<0.05) for post-hoc comparison (Tukey's HSD) to control. N=3-5. Bars±SEM.