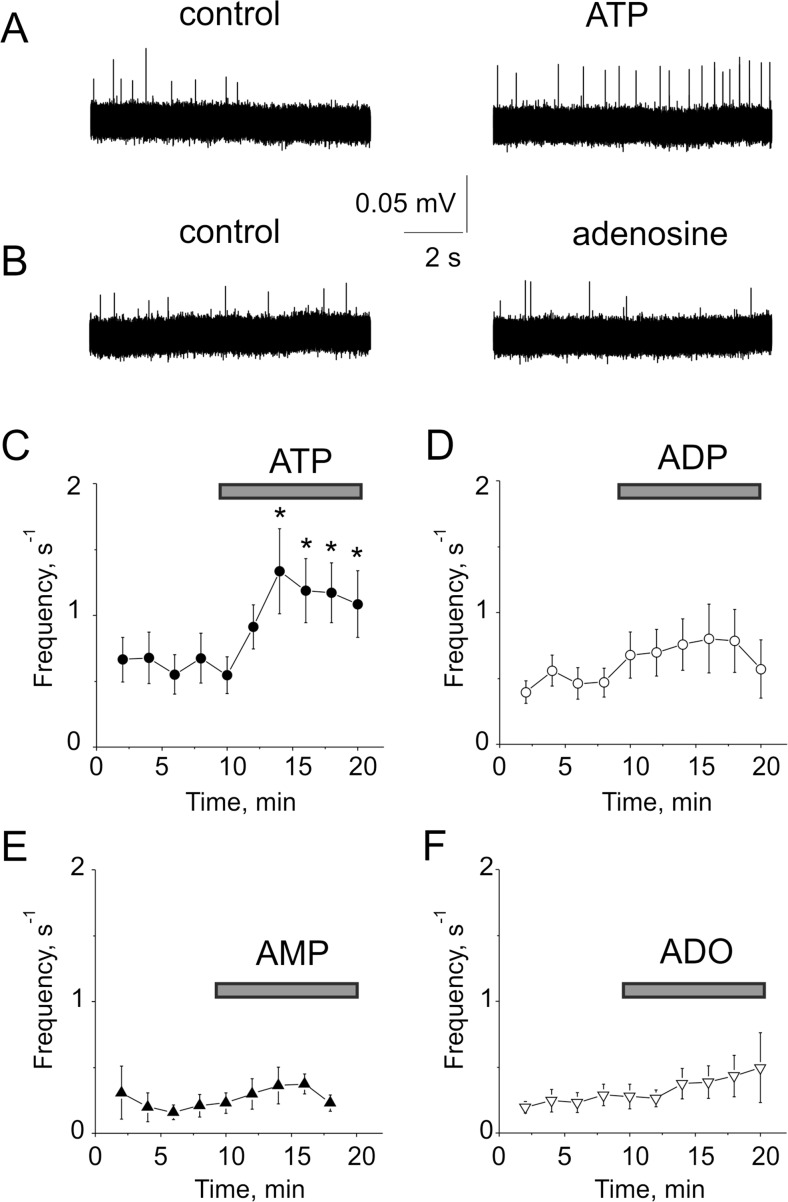
Fig. 4.
Effect of purines on trigeminal nerve spikes in the dura mater. a Representative traces of trigeminal nerve spikes in meningeal hemiskull preparation in control and after application of 100 μM ATP. Notice that extracellular ATP increased nociceptive firing in meningeal preparation. b Extracellular adenosine (100 μM) did not change significantly firing activity. c The time course of changes in the frequency of meningeal spikes after application of 100 μM ATP (n = 12 hemiskull preparations). d The time course of changes in the frequency of meningeal spikes after the application of 100 μM ADP (n = 11 hemiskull preparations). e The time course of changes in the frequency of meningeal spikes after application of 100 μM AMP (n = 6 hemiskull preparations). f The time course of changes in the frequency of meningeal spikes after application of 100 μM adenosine (n = 11 hemiskull preparations). The statistical significance was calculated in comparison with the last frequency value before applying ATP or other purines. Bars indicate duration of ATP, ADP, AMP, and adenosine applications. mean ± SEM, *p < 0.05, determined by paired t test