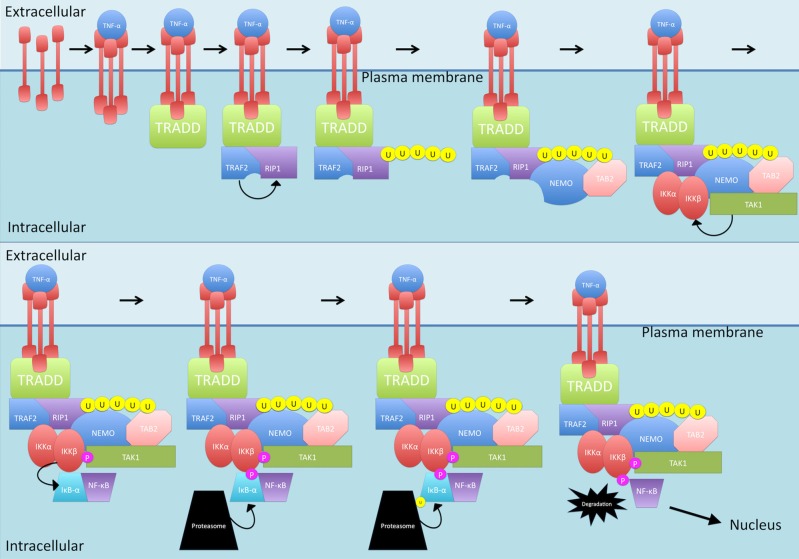
Figure 1.
The TNF-α-activated canonical nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling pathway. TNF-α triggers TNF-R1 receptor trimerization. TNF receptor type 1-associated death domain protein (TRADD) is then recruited which, in turn, recruits TNF receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2) and receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1). TRAF2 mediates K63-linked polyubiquitination of RIP1 which allows recruitment of TAB2 and NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO). Following this, TAB2 recruits transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) while NEMO and TRAF2 recruit the IKK complex. TAK1 phosphorylates IKKβ which then phosphorylates IκB-α. IκB-α is then ubiquitinated and degraded, releasing NF-κB and allowing translocation into the nucleus. P, phosphate; U, ubiquitin.