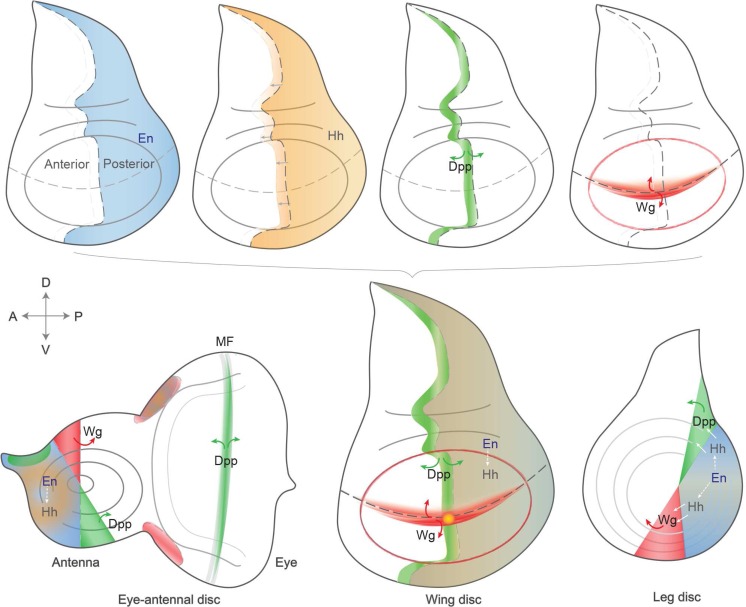
Fig. 3.
Expression domains of key signaling and patterning pathways in wing, eye-antennal, and leg discs. Imaginal discs become subdivided and patterned during development, under the concerted action of signaling pathways and morphogens. Four key signals are represented individually in the wing disc (top). Engrailed (en) is expressed in all cells in the posterior (P) compartment, conferring posterior identity and thus establishing the anterior-posterior (A-P) boundary. En directs expression of the secreted short-range signaling molecule, Hedgehog (Hh), which can cross the A-P boundary and induce expression of Decapentaplegic (Dpp). Dpp is expressed along the A-P boundary, and its secretion permits long-range signaling to direct patterning of a wider disc region. Wingless (Wg) is produced at the dorsal-ventral (D-V) boundary, a signal that is also key for wing development (see main text). The signaling domains are represented all together in the bottom central wing disc, and their roles are also similarly conserved in other tissues, like the eye-antennal (bottom left) and leg (bottom right) discs. A similar color coding is used in all discs, which are oriented with anterior to the left and dorsal up. Expression patterns at other developmental stages are described in Held (2005)