Fig. 1.
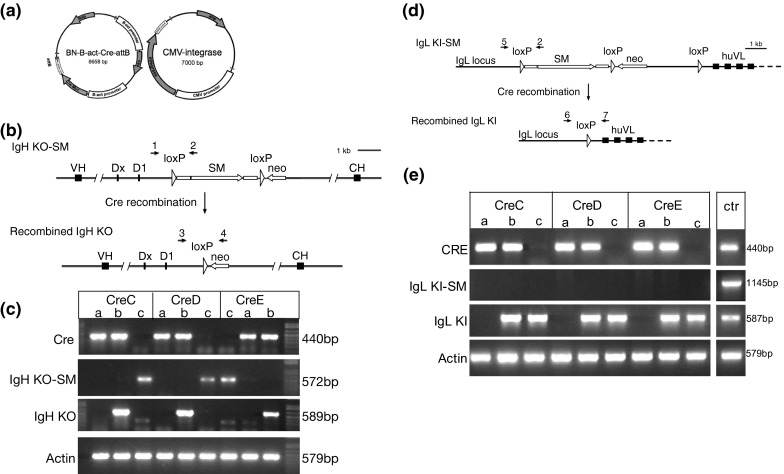
Generation of Cre recombinase transgenic chickens and removal of a selectable marker cassette. a PGCs were co-transfected with a β-actin Cre (β-actin-Neo, β-actin-Cre-recombinase, attB) and a CAG-integrase plasmid to generate stable Cre recombinase clones. b A schematic showing the heavy chain immunoglobulin knockout locus containing a selectable marker cassette (SM) between loxP sites (IgHKO-SM), and the recombined version (IgHKO). Roosters carrying the Cre recombinase transgene were bred to hens carrying IgHKO-SM. The numbers 1, 2, 3 and 4 indicate the primers that were used to evaluate the recombination in (c). c Offspring of the three Cre lines were evaluated for the ability of Cre to excise floxed transgenes. Lanes a: birds that are positive for Cre recombinase but do not carry the IgHKO transgene. Lanes b: birds that are positive for Cre recombinase show the recombined version of the IgHKO transgene. Lanes c: birds negative for the Cre recombinase have the non-recombined IgHKO-SM transgene. d A schematic showing the light chain immunoglobulin knock-in locus containing a selectable marker cassette (SM) between loxP sites (IgLKI-SM), and the recombined version (IgLKI). Roosters carrying IgLKI-SM were bred to hens carrying the Cre recombinase transgene. The numbers 2, 5, 6 and 7 indicate the primers that were used to evaluate the recombination in (e). e Offspring from Cre hens crossed to IgLKI-SM carrying roosters. Hens from three Cre lines were evaluated for their ability to excise floxed transgenes. Lanes a: birds that are positive for Cre recombinase but do not carry the IgLKI transgene. Lanes b: birds that are positive for Cre recombinase show the recombined version of the IgLKI transgene. Lanes c: birds negative for the Cre recombinase also have the recombined IgLKI transgene. ctr: positive controls for the various genes/transgenes
