Table 5.
WebLogo of predicted epitopes on E protein.
| Epitope ID | WebLogo result∗ |
|---|---|
| EP1/E |

|
|
| |
| EP2/E |

|
|
| |
| EP3/E |

|
|
| |
| EP4/E |

|
|
| |
| EP5/E |

|
|
| |
| EP6/E |

|
|
| |
| EP7/E |

|
|
| |
| EP8/E |

|
|
| |
| EP9/E |

|
|
| |
| EP10/E |

|
|
| |
| EP11/E |

|
|
| |
| EP12/E |

|
|
| |
| EP13/E |

|
|
| |
| EP14/E |

|
|
| |
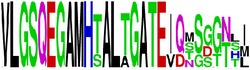
| EP15/E |
|
|
| |
| EP16/E |

|
|
| |
| EP17/E |

|
|
| |
| EP18/E |

|
|
| |
| EP19/E |

|
|
| |
| EP20/E |

|
|
| |
| EP21/E |

|
|
| |
| EP22/E |

|
|
| |
| EP23/E |

|
|
| |
| EP24/E |

|
|
| |
| EP25/E |

|
|
| |
| EP26/E |

|
|
| |
| EP27/E |

|
|
| |
| EP28/E |

|
|
| |
| EP29/E |

|
|
| |
| EP30/E |

|
|
| |
| EP31/E |

|
|
| |
| EP32/E |

|
∗The logo consists of stacks of letters, one stack for each position in the sequence. The overall height of each stack indicates the sequence conservation at that position (measured in bits), whereas the height of symbols within the stack reflects the relative frequency of the corresponding amino acid at that position. Amino acids have colors according to their chemical properties; polar amino acids (G, S, T, Y, C, Q, and N) are shown as green, basic amino acids (K, R, and H) as blue, acidic amino acids (D and E) as red, and hydrophobic amino acids (A,V, L, I, P, W, F, and M) as black.
