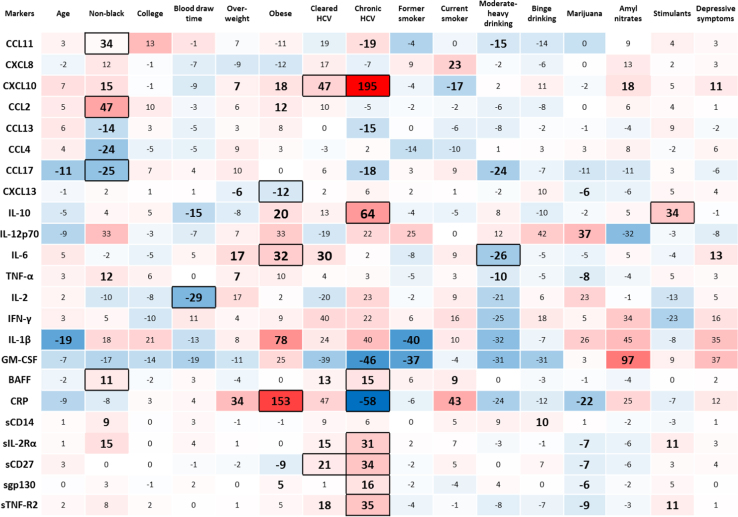
Fig. 2.
Percent differences from multivariate generalized gamma regression models examining the associations of age (10-year), non-black race, college education at baseline, blood draw time of day (P.M. versus A.M.), being overweight, obesity, cleared (antibody + only) hepatitis C infection (HCV), chronic hepatitis C infection, former smoking, current smoking, moderate-heavy alcohol consumption, binge alcohol consumption, use of marijuana, use of amyl nitrates, use of stimulants, the presence of depressive symptoms, and depression including those taking depression medication (column headings) with individual biomarkers (row headings), adjusting for persistent diabetes, persistent hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia, in a sample restricted to 2001–2009. Large bold text with black-bordered cells indicates significance at the P<0.002 level; large bold text without borders indicates marginal significance (0.002<P≤0.05). The color gradient of each cell illustrates the magnitude of the estimate (darker red indicating stronger positive percent difference and darker blue indicating stronger negative percent difference). For example, chronic HCV is associated with 64% higher concentrations of IL-10 (P<0.002) and 19% lower concentrations of CCL11 (0.002<P≤0.05).