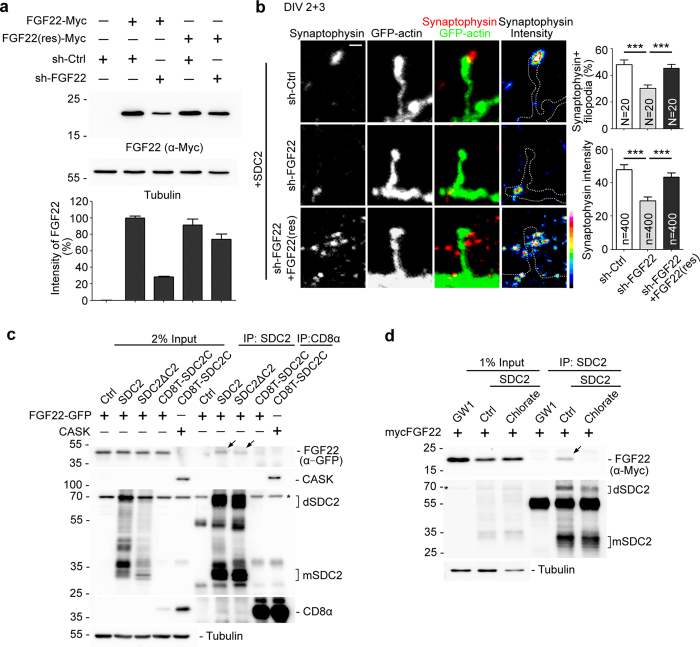
Figure 4. FGF22 interacts with SDC2 via heparan sulfate conjugates and contributes to SDC2-induced presynaptic differentiation.
(a) The knockdown effect of sh-FGF22. Neuro2A cells were transfected with various plasmids as indicated and subjected to immunoblotting using indicated antibodies. FGF22(res) is a silent mutant of FGF22 resistant to sh-FGF22 knockdown. Lower panel indicates relative intensity of Myc-tagged FGF22 normalized with tubulin. Data represent mean plus SEM. (b) Knockdown of FGF22 impairs the presynaptic differentiation induced by SDC2 at 5 DIV. The heat maps show the intensities of synaptophysin. Four hundred filopodia collected from 20 neurons were analyzed for each group. Samples were collected from two independent experiments. Error bar indicates mean plus SEM. ***P < 0.001. Scale bar: 1 μm. (c) The extracellular domain of SDC2 is required for FGF22 interaction. Neuro2A cells were co-transfected with indicated constructs and subjected to immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. (d) Inhibition of heparan sulfation by sodium chlorate (30 mM) impairs SDC2-FGF22 interaction. dSDC2: SDC2 dimer; mSDC2: SDC2 monomer. Arrows indicate the coprecipitated FGF22. Asterisk indicates the non-specific signal.