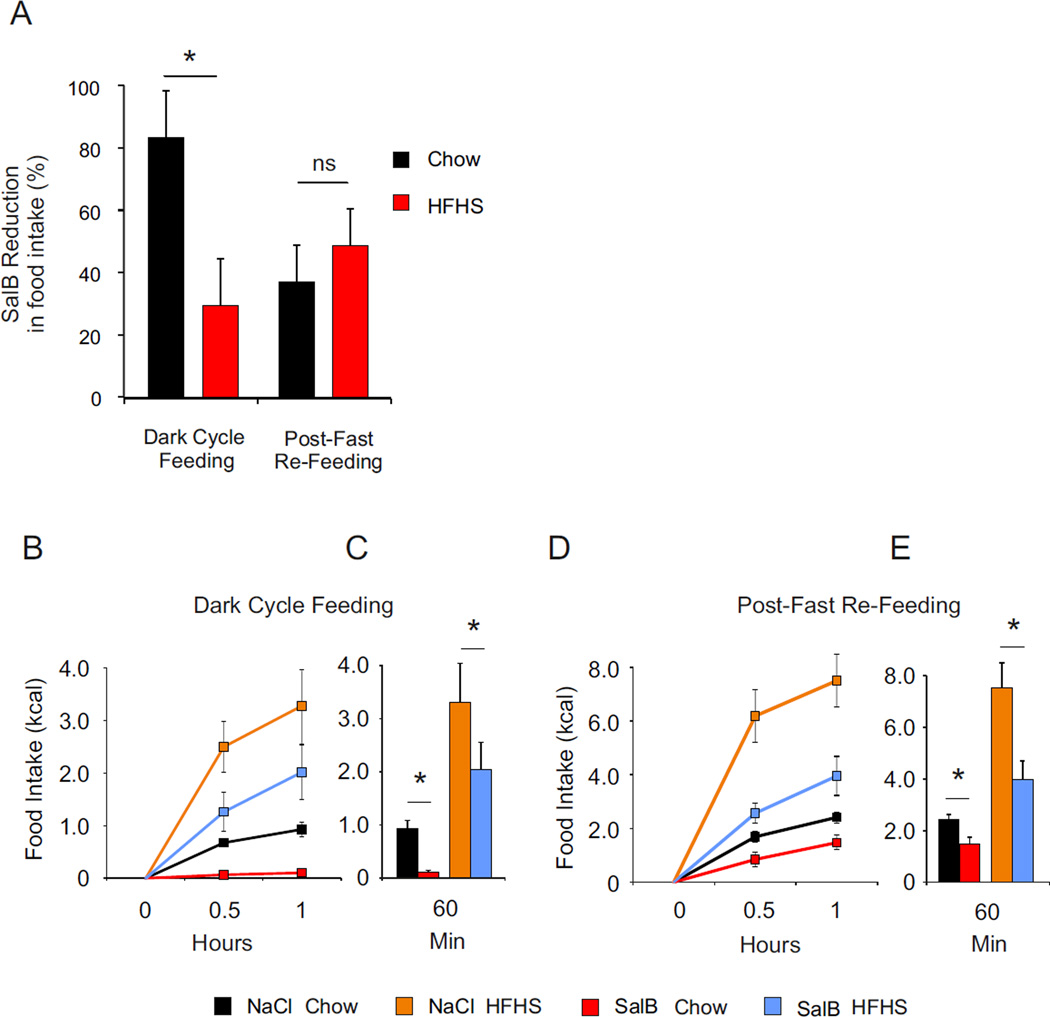
Figure 4. Acute silencing of AgRP neurons differentially impact on chow and palatable food intake.
(A) Salvorin-B (SalB) mediated inhibition of food intake in percentage over saline injection inhibition of food intake initiated for each animal. Comparison between groups was performed using analysis of variance for each paradigm. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM issue of the analysis of variance. * P<0.05 Ns = non-significant. (B, C) 2-h food intake (kcal) after onset of dark period (B, C) or after a fast (D, E). Values are expressed of mean ± SEM of animals treated with Saline or SalB under a standard and a HFHS diet. Food intake was recorded at 0.5 and 1 h. Values (C, E) are expressed as mean ± SEM at 1 h. Comparison was performed between Saline and SalB treatment using a nonparametric Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney test. * P<0.05.