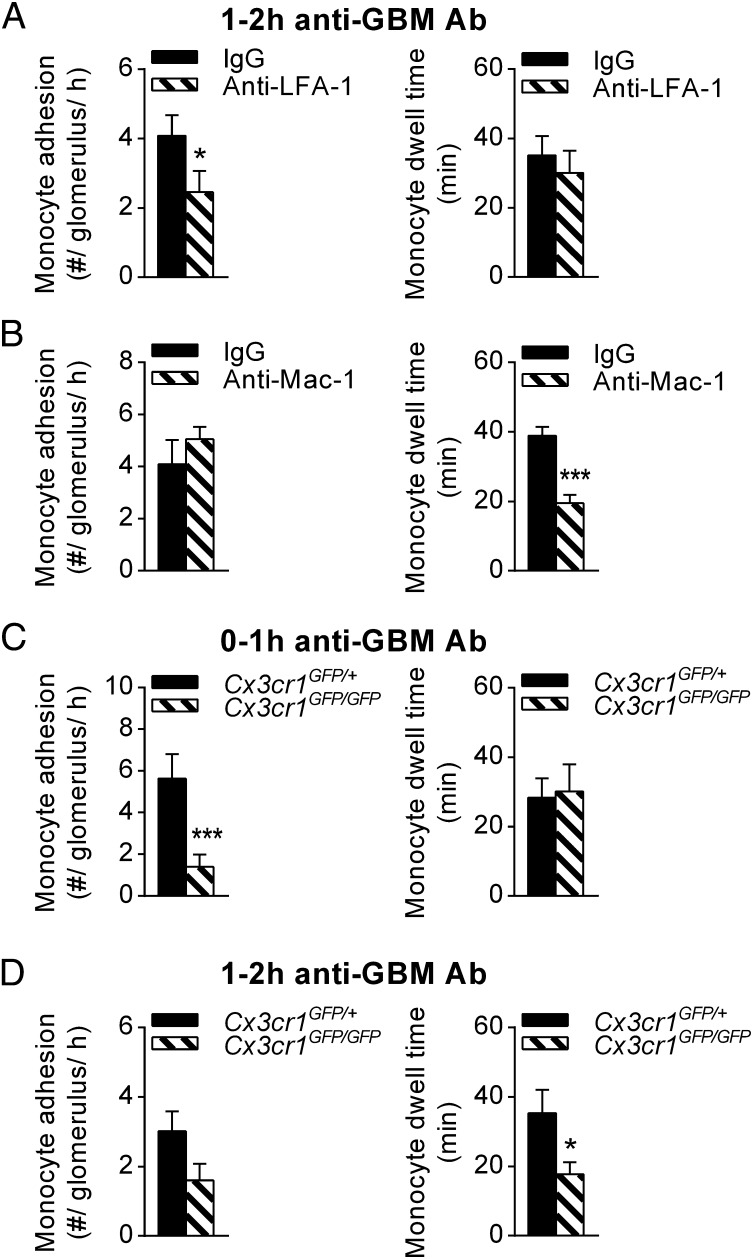
Fig. 2.
Monocyte trafficking in inflamed glomerular capillaries is dependent on CX3CR1, LFA-1 and Mac-1. The role of surface receptors in monocyte trafficking within inflamed glomerular capillaries was investigated in Cx3cr1GFP/+ and Cx3cr1GFP/GFP mice using intravital multiphoton microscopy. (A and B) Monocyte adhesion (Left), and dwell time (Right) were quantified 1–2 h after anti-GBM Ab injection in mice pretreated with either anti-LFA-1 (n = 6) (A), anti-Mac-1 (n = 6) (B), or the respective isotype controls (n = 6 and 4, respectively). (C and D) Contribution of CX3CR1 to glomerular monocyte patrolling during inflammation. Monocyte adhesion and dwell time are shown for Cx3cr1GFP/+ (n = 6) and Cx3cr1GFP/GFP mice (n = 6) 0–1 h (C) or 1–2 h (D) after anti-GBM Ab injection. Data are presented as mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 vs. corresponding control group.