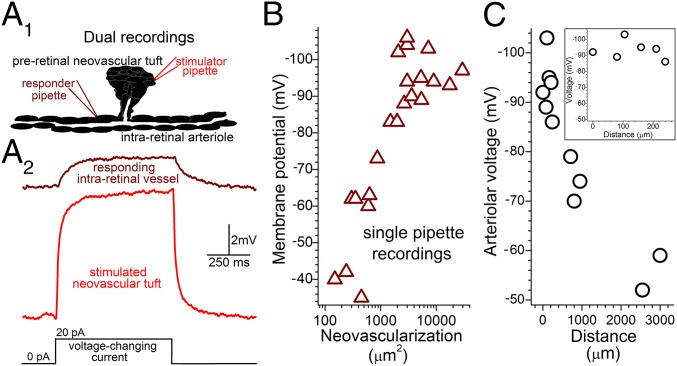
Fig. 3.
Bioelectric interactions between preretinal neovascular complexes and intraretinal vessels in ex vivo ROP retinas. (A, 1) Schematic of simultaneous dual perforated-patch recordings. (A, 2) Voltage traces from a passively monitored intraretinal vessel (Upper) and a nearby preretinal neovascular complex (Lower), whose current-induced 8.4-mV depolarization caused a 2-mV voltage decrease at the passive site. (B) Intraretinal arteriolar voltages versus amount of preretinal neovascularization ≤100 µm from the recording site. (C) Voltages of intraretinal arterioles recorded in ex vivo P17–P22 ROP retinas at locations distant from preretinal neovascular complexes. 0-µm data are from Fig. 1C. (Inset) Enlarged distance scale showing the low decay rate of voltage spreading from sites of preretinal neovascularization.