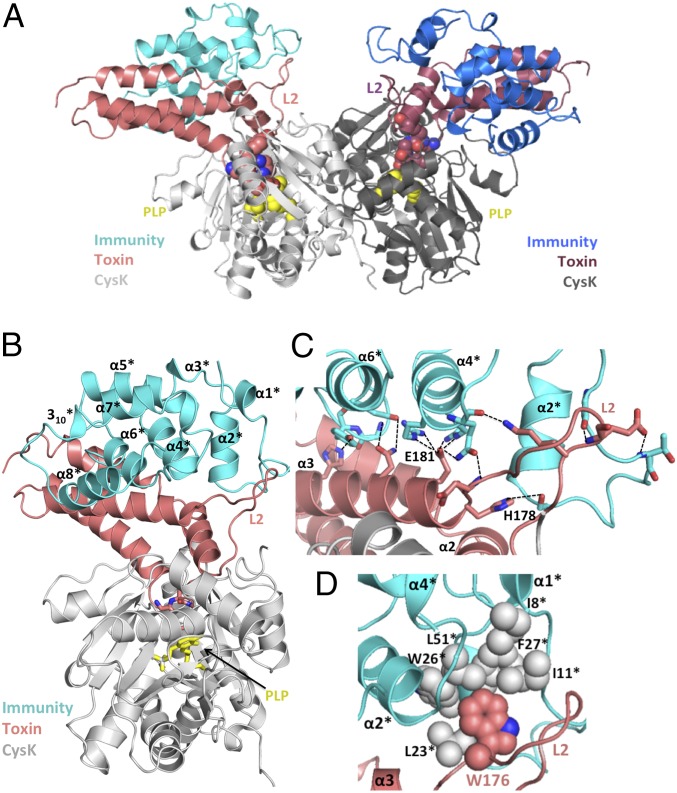
Fig. 3.
The CysK/CdiA-CT/CdiIEC536 ternary complex. (A) Crystal structure of the CysK/CdiA-CT/CdiIEC536 complex. The C-terminal GYGI peptide of CdiA-CTEC536 and CysK-bound pyridoxyl 5′-phosphate (PLP) are rendered as spheres. The ternary complex is presented in the same orientation as Fig. 1A. (B) Monomeric version of the ternary complex. CdiIEC536 secondary structure elements are outlined and indicated with superscripted asterisks (*). The C-terminal GYGI peptide of the toxin and PLP are shown as sticks. (C) H-bonding network between CdiA-CTEC536 and CdiIEC536. Interacting residues are shown in stick representation, and dashed lines indicate H-bonds. Active-site residues His178 and Glu181 from L2 and α3 of CdiA-CTEC536 interact with α2*, α4*, and α6* of CdiIEC536. (D) Hydrophobic interactions between CdiA-CTEC536 and CdiIEC536. CdiA-CTEC536 Trp176 binds into a hydrophobic pocket formed by CdiIEC536.