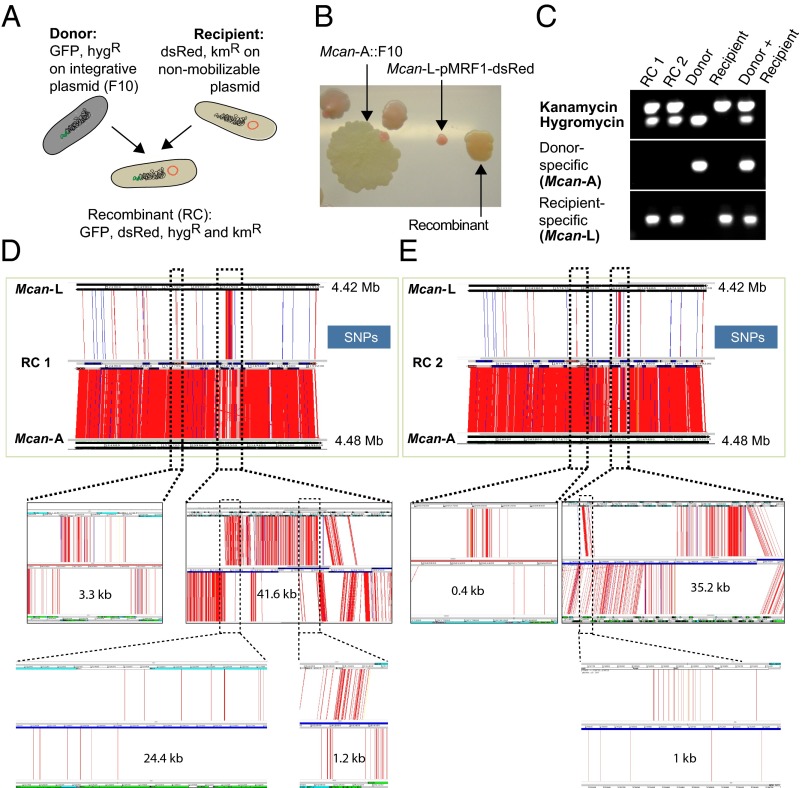
Fig. 1.
DNA exchange between M. canettii A and M. canettii L. (A) Schematic representation of donor, recipient, and recombinant strains harboring plasmids with different antibiotic cassettes and genes encoding fluorochromes. (B) Differently colored KmR and HygR colonies corresponding to a spontaneously KmR M. canettii A::F10 donor strain, some spontaneously HygR M. canettii L pMRF-dsRed recipient strains, together with orange colored colonies that represent double-resistant putative recombinants, which have obtained the GFP-expressing gene cluster from the donor. (C) Results from PCR analysis of two recombinants, the donor M. canettii A and the recipient M. canettii L with oligonucleotides amplifying either the kanamycin or the hygromycin resistance cassettes as well as genes specific for the donor or the recipient strain. (D and E) ACT visualization of SNPs identified between two recombinant (RC) genomes (middle genome of each image) and either the donor M. canettii A (bottom) or the recipient M. canettii L genome (top). A selection of the transferred sequence blocks are enlarged (dotted lines) for better visualization of the donor-derived segments. SNPs are represented by red and indels by blue lines.