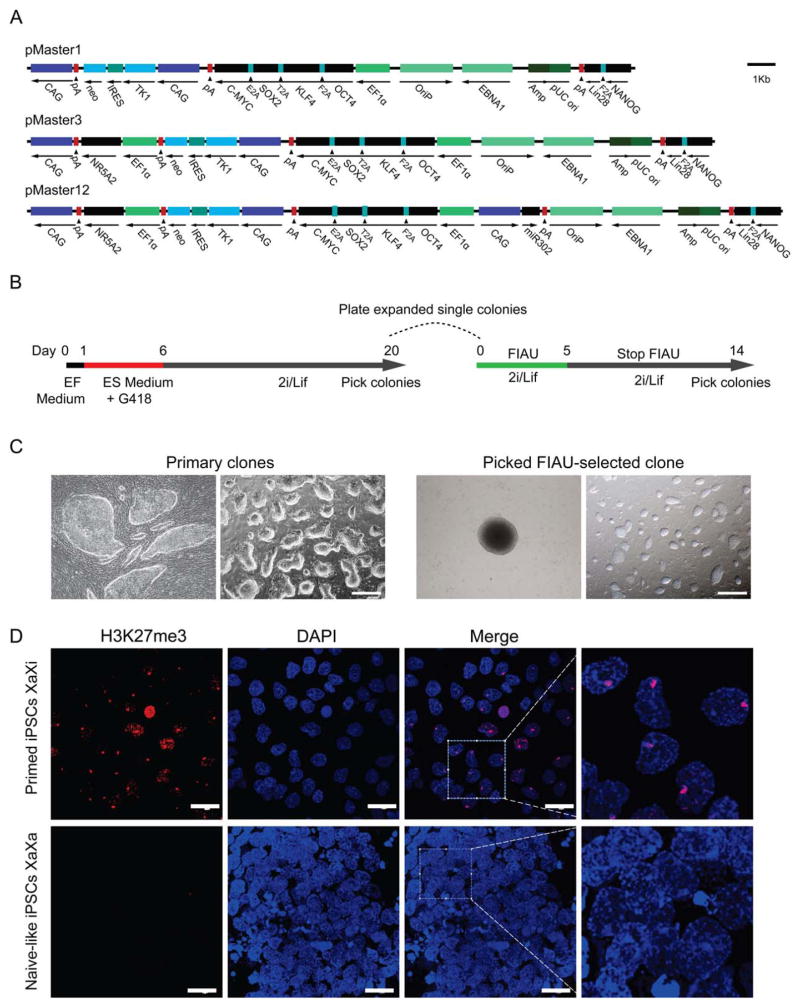
Figure 1.
Derivation of porcine iPSCs using episomal plasmids. (A): Schematic representation of the episomal reprogramming vectors. The pMaster1 vector contains six human reprogramming genes (OKSM+NANOG+LIN28); pMaster3 has seven genes (OKSM+NANOG+LIN28+NR5A2); pMaster12 has eight genes (OKSM+NANOG+LIN28+NR5A2+miR302/367 cluster). The neo and HSVtk resistance genes are separated by IRES sequences. (B): Outline of reprogramming mediated by pMaster vectors. EF medium, serum-based embryonic fibroblast medium; ES medium, serum/Lif-based ESC medium; 2i/Lif, serum-free ESC medium supplemented with PD0325901, CHIR90021 and Lif. (C): Bright-field image of porcine iPSCs derived with the pMaster12 vector. Primary iPSC clones obtained 6 days and 20 days after transfection; FIAU-resistant iPSC clone picked at day 14 showed an undifferentiated ESC-like morphology by expansion at serial passages. Scale bars =500 μm. (D): Immunostaining for H3K27me3 in primed and naïve-like porcine iPSCs. Histone H3K27 trimethylation spots were observed in primed porcine iPSCs (pM12-6-2, P6) cultured in serum/KOSR medium but not in naive-like iPSCs cultured in 2i/Lif medium. Scale bars =50 μm. Abbreviations: EF, embryonic fibroblast; ESC, embryonic stem cell; FIAU, Fialuridine; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells.