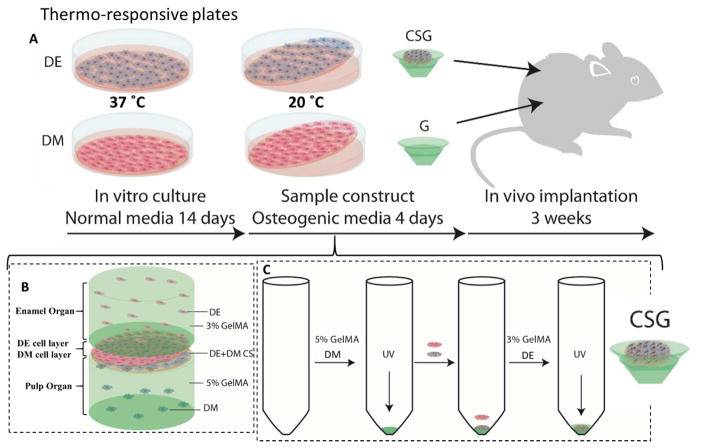
Figure 1. Experimental design and culture of 3D GelMA-CS tooth buds.
A. DE and DM cells were seeded on thermo-responsive plates and cultured in normal DE and DM media, respectively, for 14 days. DE and DM CSs were detached by temperature reduction (20ºC) and layered over GelMA constructs to create experimental 3D tooth bud constructs (CSG = DE and DM CSs layered over dental cells encapsulated in GelMA; G = GelMA alone). For in vivo analyses, replicate constructs were cultured in osteogenic media for 4 days and implanted subcutaneously onto the backs of the rats. B. Bioengineered 3D CS - GelMA tooth bud model. The bottom layer mimics the pulp organ (5% GelMA encapsulating DM cells) and the top layer mimics the enamel organ (3% GelMA encapsulating DE cells). The DE and DM CS layers mimic polarized DE-DM cell layers normally observed in developing teeth. C. Steps used to prepare the constructs. DM cells (3×107 cells/ml) were re-suspended in 100 μL of 5% GelMA and photo-crosslinked. DM and DE cell sheets were layered over the polymerized DM 5% GelMA. DE cells (3×107 cells/ml) re-suspended in 100 μL 3% GelMA and 100 μL, layered over construct and photo-crosslinked.