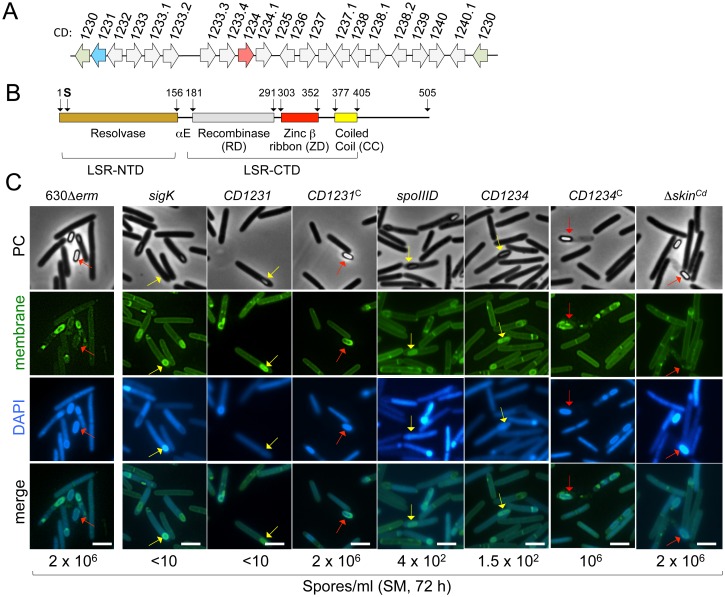
Fig 1. The skinCd gene CD1231, coding for a serine recombinase, is required for sporulation.
A: schematic representation of the sigK-skinCd region of the C. difficile 630Δerm chromosome. The two halves of the sigK gene (5‘ and 3’ part of CD1230) are shown in green, and the CD1231 gene, coding for a protein of the large serine recombinase family is shown in blue. The CD1234 gene is shown in pink. B: domain organization of the CD1231 serine recombinase. The horizontal black line is a linear representation of the amino acid sequence. The three conserved domains identified are color-coded: brown, resolvase domain (PF00239, which forms the N-terminal domain (NTD); grey, recombinase domain (RD; PF07508); red, a zinc ribbon domain (ZD; PF13408); yellow, a coiled-coil (CC) motif. The recombinase domain, the zinc finger and the coiled-coil form the C-terminal domain (CTD). A long α-helix linking the NTD and CTD domains is indicated as αE. The catalytic serine, close to the N-terminal end of the protein, is represented. C: cells of the WT strain 630Δerm, the ΔskinCd, spoIIID, sigK, CD1231 and CD1234 mutants and the complemented strains, CDIP533 and CDIP397, carrying multicopy alleles of CD1231 (CD1231C) or CD1234 (CD1234C) expressed under the control of their native promoters were collected after 24 h of growth in liquid SM, stained with the DNA stain DAPI and the membrane dye MTG and examined by phase contrast and fluorescence microscopy. The red arrows point to phase bright spores and the yellow arrows to phase grey spores. Scale bar, 1μm. The titer of heat resistant spores measured for each strain after 72 h of growth in SM is indicated below the panels. The titer of heat resistant spores at 48 h was 0.75 x 106 for strain 630Δerm and for the ΔskinCd mutant.