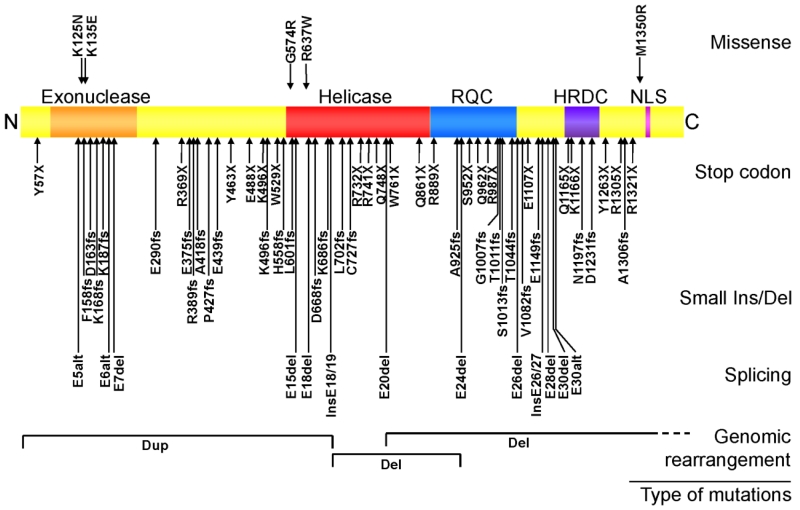
Fig. 2.
WRN disease mutations in classical WS patients. The rectangular box shows the WRN protein. Known functional domains are: exonuclease region (Exo), helicase region, RecQ C-terminus consensus region (RQC), helicase and RnaseD consensus region (HRDC) and the nuclear localization signal (NLS). Disease mutations are grouped based on the types of mutations. Splicing mutations that result in identical exon skipping are combined and indicated by the number of unique mutations as in (2). Splicing mutations that create new splice sites are indicated as “nss”. Modified from (Friedrich et al., 2010).