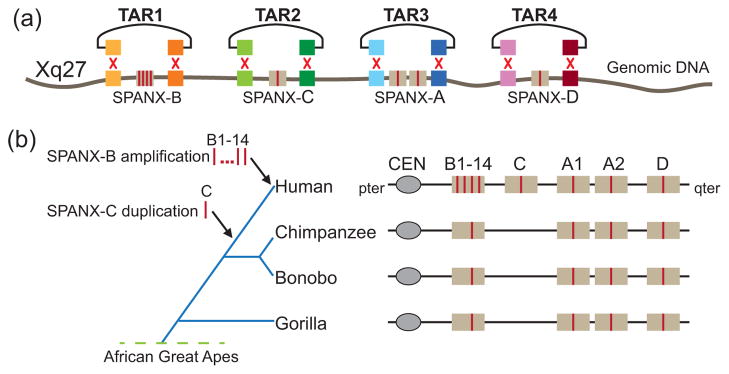
Fig. 4.
Organization of the SPANX genes in primates. Syntenic genomic fragments containing different members of the SPANX gene family from the human, chimpanzee, bonobo, gorilla, orangutan, and macaque were isolated by TAR cloning. Unique targeting hooks in the TAR vectors were chosen from the available human genome sequences. Comparison of the sequences showed that TAR clones from chimpanzee, bonobo, and gorilla do not contain SPANX-C along with the duplication. In addition, the amplification of SPANX-B from one to 14 copies in different individuals is also human specific. The SPANX-A/D gene family is absent in the orangutan and macaque.