Fig. 1.
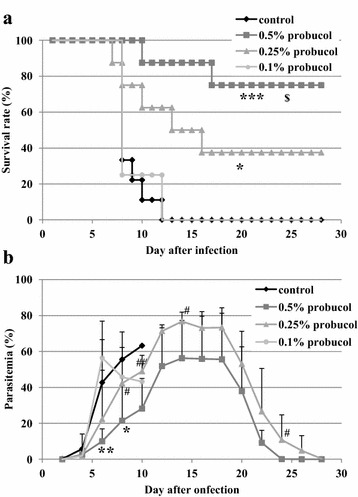
Effect of probucol on Plasmodium yoelii XL-17 infection in mice. C57BL/6 J mice were fed with 0.1 % (w/w), 0.25 % (w/w) and 0.5 % (w/w) probucol mixed diet from 2 weeks before infection to through infection period. Plasmodium. yoelii XL17 (4 × 104 iRBC/head) were inoculated into drug-treated mice and control mice fed with regular commercial diet by intraperitoneal injection. Survival rate (a) and parasitaemia (b) were monitored for 28 days post infection. Control, n = 9; 0.5 % probucol, n = 8; 0.25 % probucol, n = 8; 0.1 % probucol, n = 4. The data presented are mean ± SD. Compared with control mice: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005. Compared with 0.5 % probucol-treated mice:, # p < 0.1, ## p < 0.05. Compared with 0.1 % probucol-treated mice: $ p < 0.005
