FIGURE 3.
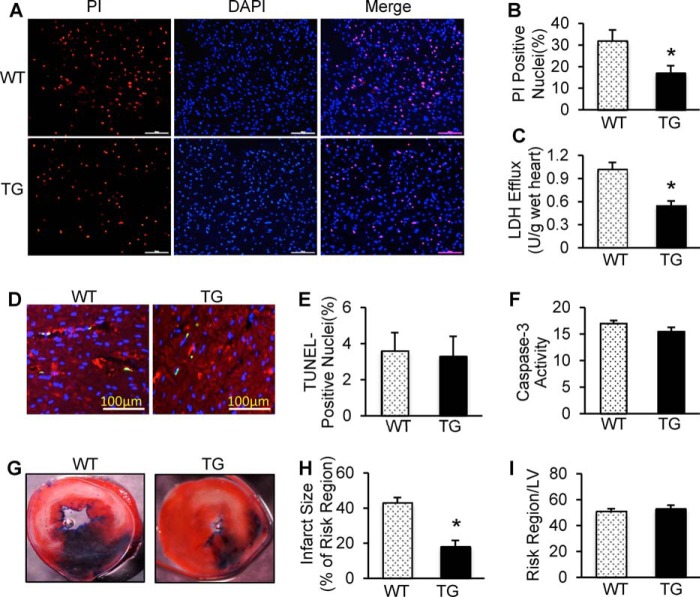
Overexpression of miR-223-3p/-5p duplex attenuated I/R-induced myocardial necrosis and infarction size. A, PI was perfused into the mouse heart to label necrotic cells at the end of ex vivo I/R (45 min/1 h). Red, PI-positive nuclei; blue, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole-stained nuclei. Scale bars, 100 μm. B, quantitative analysis of myocardial necrotic cells in ex vivo I/R hearts (n = 8 for WT; n = 7 for TG group; *, p < 0.05 versus WTs). C, total LDH was measured in coronary effluent collected during the first 10 min of reperfusion (n = 8 for WT; n = 7 for TG group; *, p < 0.05 versus WTs). D and E, representative images (D) and quantitative results (E) of the TUNEL staining assay in WT and TG hearts after ex vivo I/R (45 min/1 h). Green, TUNEL-positive nuclei; red, α-actin; blue, DAPI. Scale bars, 100 μm. F, Caspase-3 activity was similar between TG hearts and WT hearts subjected to ex vivo I/R. p > 0.05 versus WTs (n = 6 hearts per group; p < 0.05 versus WTs). G–I, overexpression of miR-223-3p/-5p duplex greatly reduced in vivo myocardial infarct size after 30 min of left anterior descending artery occlusion followed by 24 h of reperfusion. The mouse hearts were stained by Evans Blue and triphenyltetrazolium chloride after in vivo I/R. White/gray, infarct size; red, area at risk; and blue, non-ischemic LV (n = 8 for WT; n = 10 for TG group; *, p < 0.01 versus WTs). Error bars represent mean ± S.D.