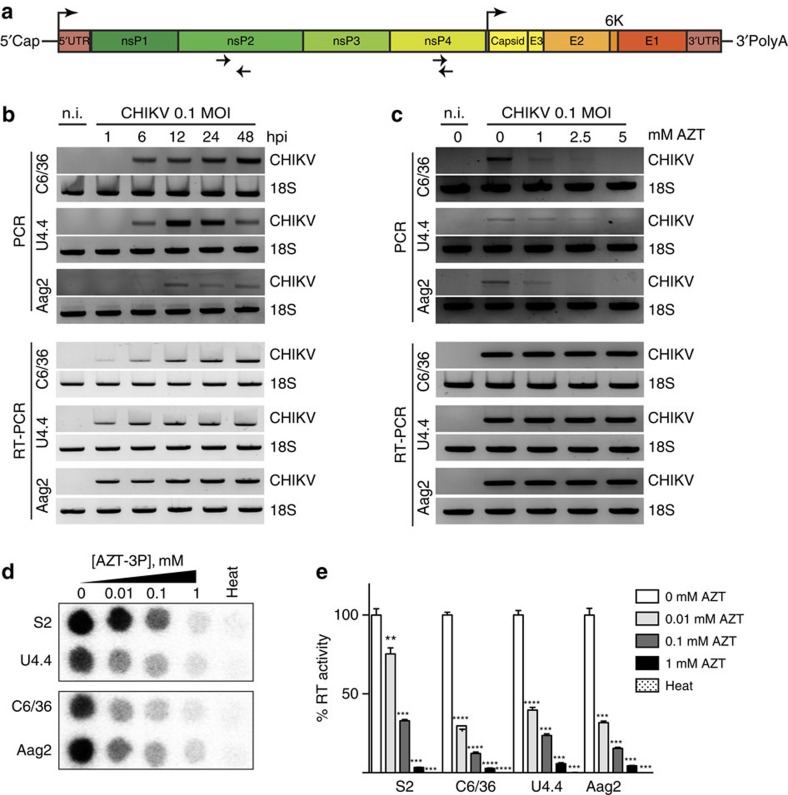
Figure 1. Mosquito cells produce host reverse transcriptase-dependent arbovirus-derived DNA.
(a) Schematic of CHIKV viral genome. Top arrows indicate the position of the genomic and subgenomic promoters. Bottom arrows indicate the position of the primers used for vDNA detection. (b) Kinetics of vDNA synthesis. C6/36, U4.4 and Aag2 cells were infected with CHIKV at a MOI of 0.1 and cells were harvested at the indicated time points. Cells were analysed by PCR (upper panel) for vDNA detection. RT-PCR (lower panel) was used to follow viral infections. Non-infected cells (n.i) were used as a negative control and cellular 18S rRNA was used as a housekeeping gene loading control. (c) AZT inhibits vDNA synthesis in vitro. C6/36, U4.4 and Aag2 cells were treated with increasing concentration of AZT for 2 days. At the indicated time point, cells were harvested and vDNA and RNA were assessed as described in b. (d–e) Endogenous reverse transcriptase activity in insect cells. (d) Dose-dependent AZT inhibition was tested in insect cell extracts and (e) quantification of reverse transcriptase inhibition expressed as an activity percentage of non-treated extracts. Heat inactivated samples (heat) were used as negative controls. Drosophila S2 cells were used as a positive control. Each experiment was completed at least 3 times. Error bars correspond to the s.d. t-test with Welch's correction was used to determine statistical significance compared with the untreated control as a reference (**P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001).