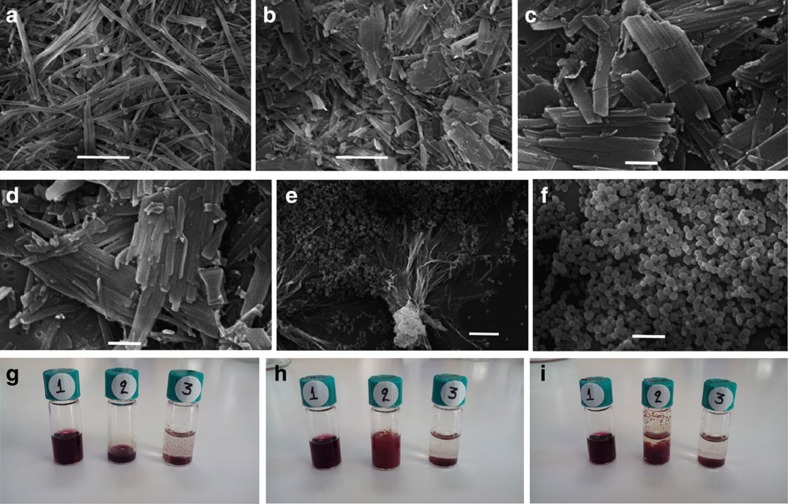
Figure 2. Changes in the morphology of Fmoc-FLFL-TPP with the solvent composition.
Samples observed in SEM following critical point drying of Fmoc-FLFL-TPP dissolved in dry dichloromethane which was injected into n-heptane at room temperature. Final relative ratios (v/v) of CH2Cl2 to n-heptane were: (a) 3:7; (b) 2:8; (c) and (d) same sample as in b imaged at higher magnification with sideways associated fibrils. (e,f) 5:5. Further SEM micrographs at 3:7 and 2:8 concentrations are shown in the Supplementary Fig. 19. Scale bars, 5 μm in a,b,e; 2 μm in f; 1 μm in c,d. Pictures of vials showing Fmoc-FLFL-TPP in the following conditions: (g) immediately after addition of: 1 ml pure dichloromethane (vial 1); 0.2 ml pure dichloromethane (vial 2); 1 ml pure n-heptane (vial 3). (h) immediately after addition of 0.8 ml heptane to vial 2. (i) Twenty-four hours after addition of 0.8 ml n-heptane to vial 2. The final concentration of Fmoc-FLFL-TPP in all conditions was 1 mM. A clear solution is observed for the sample dissolved in pure dichloromethane, while in pure n-heptane a rapidly sedimenting precipitate is formed. Following addition of n-heptane to the dichloromethane-dissolved sample in vial 2, turbidity rapidly ensues and a slowly sedimenting precipitate is formed.