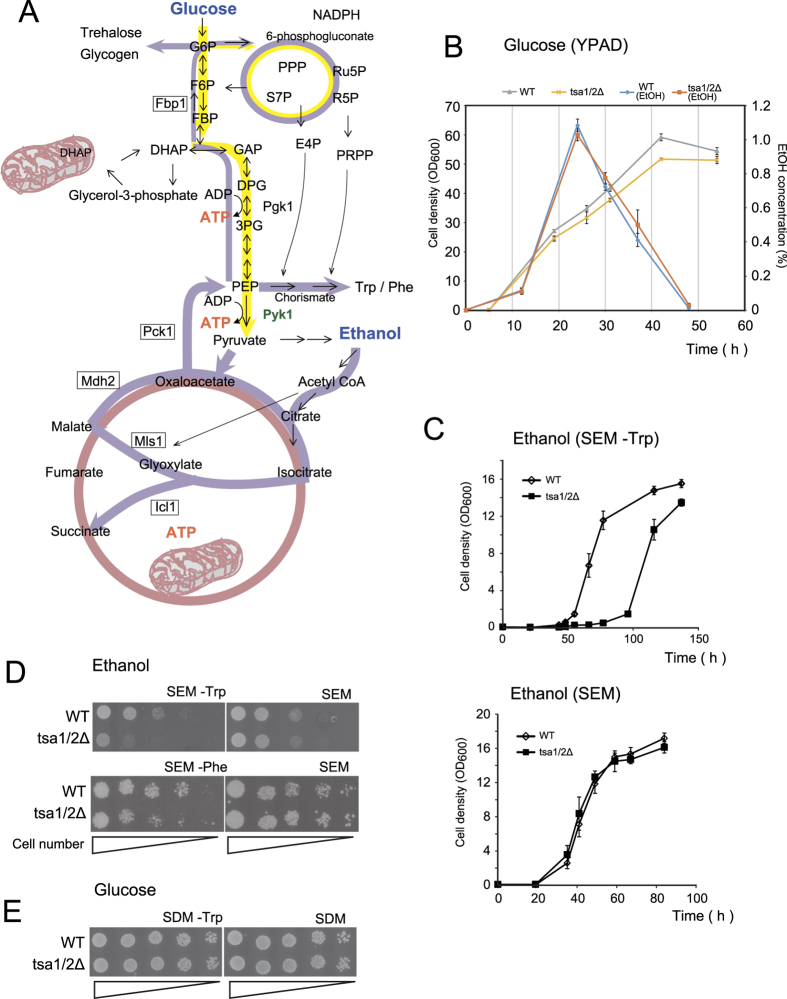
Figure 1. Loss of Tsa1/2 promotes growth suppression in Trp- or Phe-free ethanol medium.
(A) Schematic representation of glucose (yellow arrows) and ethanol (purple arrows) carbon metabolism. Glycolysis metabolites are abbreviated as follows: glucose 6-phosphate (G6P), fructose 6-phosphate (F6P), fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP), dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP), 1,2-diphosphateglycerate (DPG), 3-phosphoglycerate (3PG) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP). Metabolites in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) include 6-phosphogluconate, ribulose 5-phosphate (Ru5P), ribose 5-phosphate (R5P), sedoheptulose 7-phosphate (S7P), erythrose 4-phosphate (E4P) and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). Trp/Phe synthesis begins with PEP and E4P via chorismate. Utilization of two-carbon compounds such as ethanol and acetate require the glyoxylate cycle and gluconeogenesis (purple arrows). The glyoxylate cycle plays an anaplerotic role in the provision of metabolites to produce essential compounds in the cytoplasm. The key enzymes of the glyoxylate cycle, isocitrate lyase (Icl1) and malate synthase (Mls1), as well as malate dehydrogenase (Mdh2), are upregulated in yeast in response to the ethanol carbon source and are expressed in the cytoplasm (http://www.yeastgenome.org/). Gluconeogenesis uses most of the enzymes that are common to glycolysis, except during the steps responsible for the synthesis of PEP and F6P, which are catalyzed by phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase (Fbp1), respectively. The tricarboxylic acid TCA cycle is indicated by a bright red-colored circle. (B) Growth curves and changes in ethanol levels of wild type (WT, gray and blue lines, respectively) and tsa1/2∆ (yellow and orange lines, respectively) in glucose-rich medium (YPAD). Ethanol was measured using F-Kit Ethanol (J.K. International, Tokyo, Japan). (C) Growth curves of wild type (open diamonds) and tsa1/2∆ (closed square) cells, neither of which are Trp/Phe-auxotrophs, growing in Trp-free ethanol medium (SEM –Trp) and Trp-containing ethanol medium (SEM). The data are presented as the mean +/− standard error of the mean (N = 3). (D,E) Spot assays were performed on wild type (WT) and tsa1/2Δ cells prepared in SDM culture (early stationary phase, 3 days). A series of one-fifth dilutions of 5 × 104 cells were spotted on agar plates (SEM –Trp, SEM –Phe, SEM, SDM –Trp, and SDM). See also Figure Supplement 1.