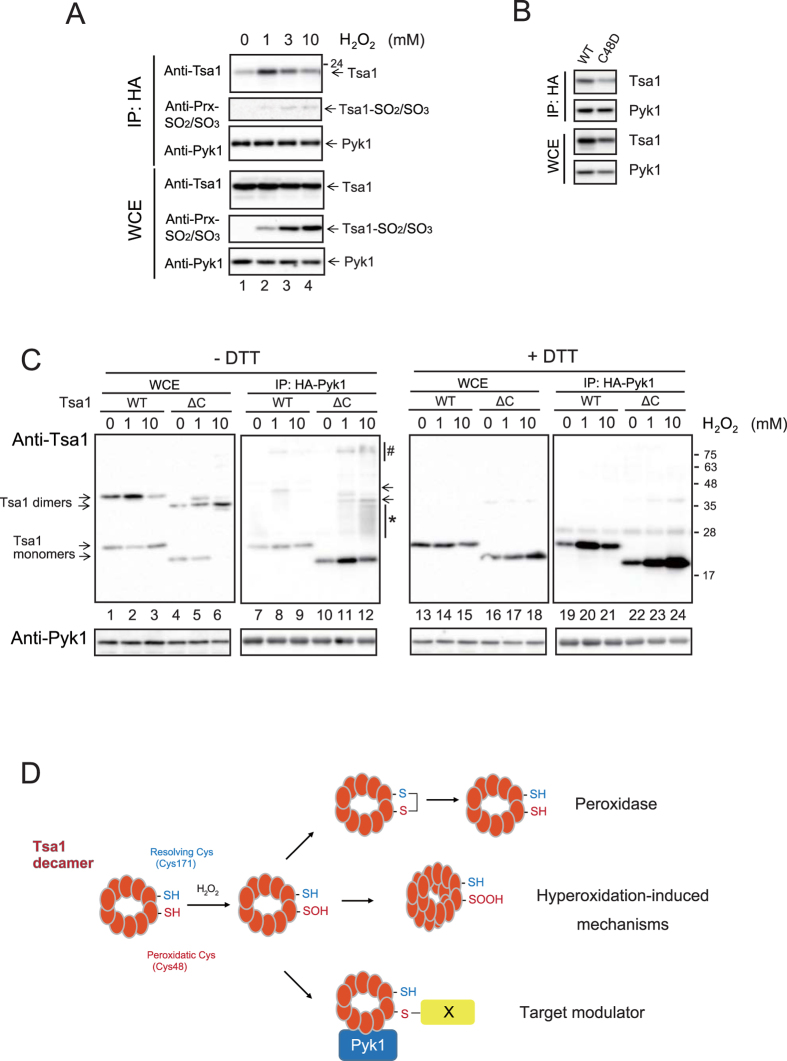
Figure 7. Oxidation status of Tsa1 Cys48 required for the H2O2-induced interaction with Pyk1 in early stationary phase cells.
(A) The H2O2 concentration-dependent interaction and hyperoxidation of Cys48 were examined. pyk1∆ cells carrying an expression vector for HA-Pyk1 were cultured to early stationary phase (3 days) in SD and treated with 1 or 3 or 10 mM H2O2 for 10 min. Cell lysate preparation and IP were performed as described above. IP fractions and WCE were treated with DTT and immunoblotted using anti-Tsa1, anti-Prx-SO2/SO3 and anti-Pyk1 antibodies. The anti-Prx-SO2/SO3 antibody reacts with sulfinic acid and sulfonic acid of Tsa1-Cys48. The positions of Tsa1, Tsa1-SO2/SO3 and Pyk1 are indicated by arrows on the right side of the panels. (B) The interaction of Pyk1 with Tsa1C48D was examined. (C) Tsa1/2∆ pyk1∆ cells carrying expression vectors for HA-Pyk1 and Tsa1 or a hyperoxidation-resistant mutant of Tsa1 (Tsa1∆C; ∆C) were treated with or without H2O2 (the concentration is indicated in the figure) for 10 min. WCE (lanes 1 to 6 and lanes 13 to 18) and IP fractions (lanes 7 to 12 and lanes 19 to 24) were treated with (lanes 13 to 24) or without (lanes 1 to 11) DTT, and immunoblotted using anti-Tsa1 and anti-Pyk1 antibodies. (D) The three independent functions of Tsa1, namely, thioredoxin (Trx)-dependent peroxidase, hyperoxidation-induced functions (such as in molecular chaperones) and redox-induced modulator of Pyk1, are presented diagrammatically. Formation of mixed disulfide bond with unknown ‘X’ proteins enhanced the interaction of Tsa1 with Pyk1.