Fig. 1.
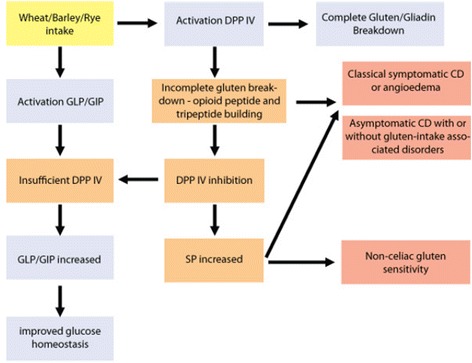
The development of symptomatic and asymptomatic CD and NCGS. Incomplete gluten breakdown results in inhibition of DPP IV and the possible increase of SP, leading to intestinal and extra-intestinal gluten-induced disorders. Gluten-derived DPP IV inhibition also increases the presence of GIP and GLP in the gut, leading to improved glucose homeostasis
