Fig.6.
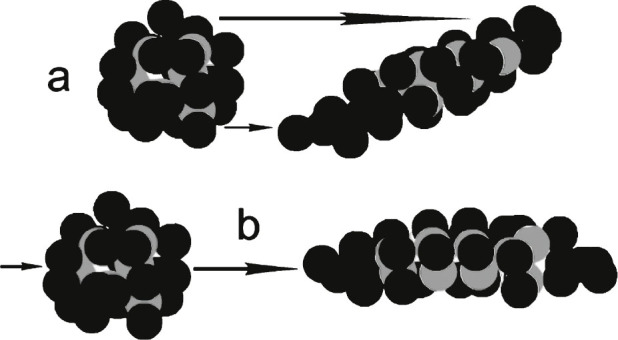
Hypothetical protein showing gray balls as hydrophobic groups and black balls as hydrophilic groups. The protein in (a) has undergone severe laminar shear to emphasize the resulting increased exposure of hydrophobic groups to the surrounding solvent. The same is true in (b) for extensional shear, where the molecule is essentially pulled lengthwise. Models are purely hypothetical. Energy is added to the molecule in both (a) and (b) forming unstable molecules. Most brain shear events probably have contributions of both (a) and (b) types of shear.
