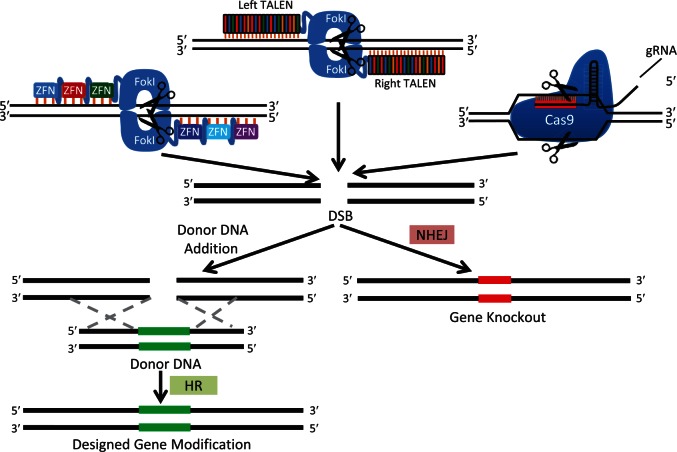
Figure 2.
Three most common gene modification strategies using designer nucleases (ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas).
The given nuclease system identifies a specified region of the genome through base pair recognition (orange hash marks) and creates a DSB (scissor). In the absence of a repair donor, NHEJ DNA repair creates an ‘indel’ (red DNA region) resulting in a gene knockout. If a repair donor is supplied, HR may occur, resulting in incorporation of a designed modification (e.g. insertion, deletion, substitution).
Cas, CRISPR associated protein, CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats; DSB, double strand break; gRNA, guide-RNA; HR, homologous recombination; NHEJ, nonhomologous end-joining; TALEN, transcription activator-like effector nuclease; ZFN, zinc-finger nuclease.