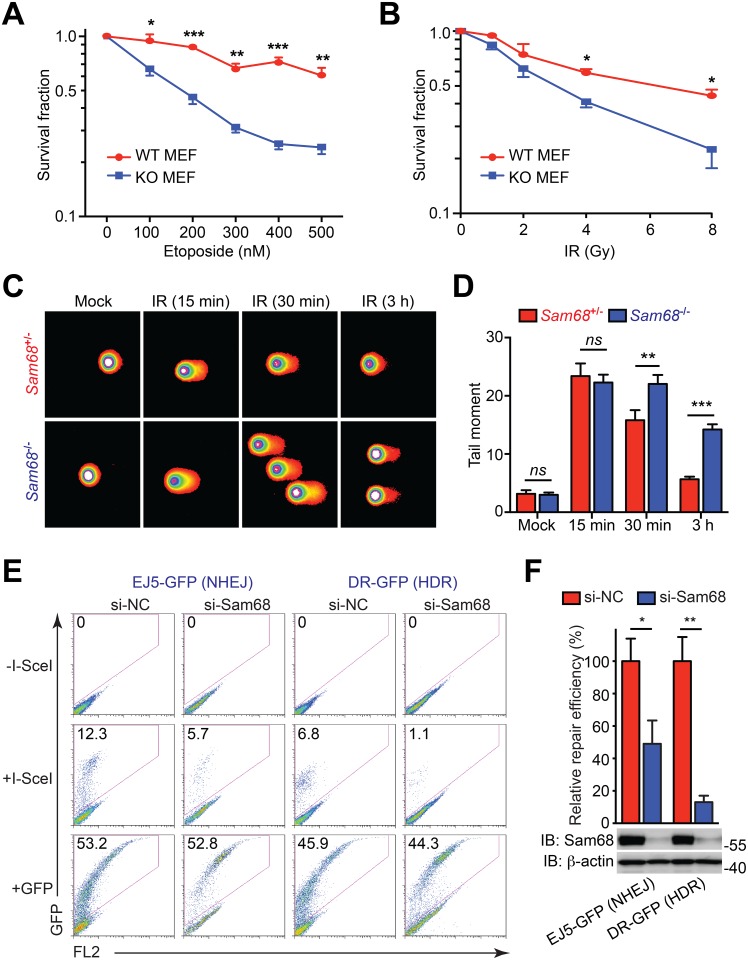
Fig 1. Sam68 is required for repairing DNA strand breaks.
(A, B) Survival fraction of wild-type (WT) and Sam68 knockout (KO) mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) 96 h post treatment with indicated concentrations of etoposide for 20 h (A) or indicated doses of γ-irradiation (IR) (B). (C) Representative microphotographs of alkali comet assay of Sam68+/- and Sam68-/- thymocytes at indicated time points following 4 Gy of IR or mock-treated. (D) Quantification of tail moments in C, with summarized data from 40–60 cells within 15 random fields for each time point. (E) Flow cytometric detection of effect of Sam68 knockdown on DNA damage repair efficiency. U2OS reporter cell lines specifically designed to repair DNA damage through nonhomologous end joining (NHEJ) and homology-directed repair (HDR), were transfected with nonspecific control (si-NC) or Sam68-specific (si-Sam68) small interference RNA, together with (+) or without (−) I-SceI plasmid, or green fluorescent protein (GFP) control. Shown are representative flow cytometry analyses of the frequency of GFP+ cells in indicated reporter cell lines 72 h following transfection. (F) Quantification of relative repair efficiency (normalized to si-NC and I-SceI cotransfected cells) in indicated reporter cell lines, summarized from three independent experiments. The Sam68 knockdown efficiency was examined by immunoblot (IB), with β-actin as a loading control, in indicated reporter cell lines (bottom). Results in (A), (B), (D), and (F) are expressed as mean and standard error of the mean (SEM). ns, nonsignificant difference; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by Student’s t tests. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Underlying data are shown in S1 Data.