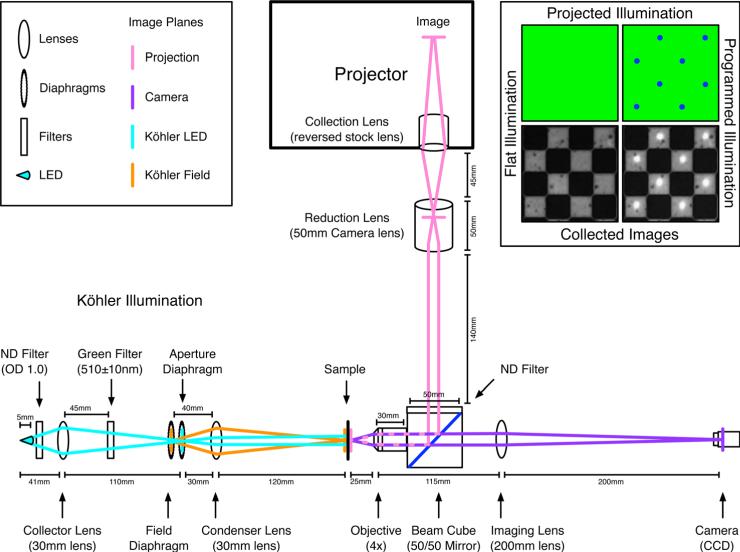
Fig. 9.
The optical layout of the PIM with distances between elements. The different optical paths are shown in pink, purple, and cyan with an additional conjugate path in orange. The original projection image from within the projector is focused onto the sample via the pink path with an intermediate image plane within the body of the reduction lens. The sample is imaged onto the camera via the purple path. The Köhler illumination is created via the cyan path with an intermediate image plane on the aperture diaphragm and the conjugate field path is shown in orange. The field diaphragm controls the field of illumination and the aperture diaphragm controls the intensity of illumination. The neutral density filters attenuate the intensity of the projector and LED while the 510 ± 10-nm bandpass “green” filter is used to select illumination wavelength. The locations of the filters are not critical as long as imaging planes are avoided. Shown in the corner are examples of flat illumination and programmed illumination illuminating the 100-μm checkerboard alignment grid.