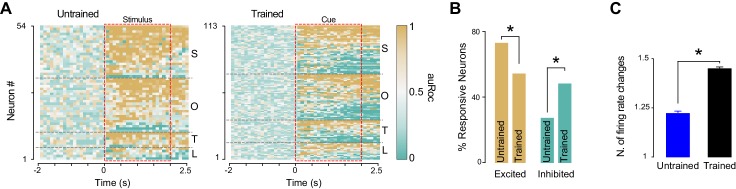
Figure 5. Time course of GC responses in the groups of trained and untrained rats.
(A) Population plot of all GC neurons modulated by at least one cross-modal stimulus in untrained (left panel) and in trained (right panel) rats. Each row represents a GC neuron. The color of each square along the x-axes (see color bar) represents the normalized firing rate within each 200 ms bin. The red dotted rectangular box indicates stimulus presentation. Neurons are clustered by the sensory modality (S for somatosensory, O for odor, T for tone and L for light) and ranked with excitatory and inhibitory responses from top to bottom respectively. (B) Histograms showing the percentage of cue responsive neurons that are excited and inhibited by anticipatory cues. (C) Histogram showing the average number of firing rate modulations in neurons responsive to cross-modal stimuli. Asterisk indicates p<0.05 for test for equality of proportion and t-test for panel B and C respectively.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.16420.014