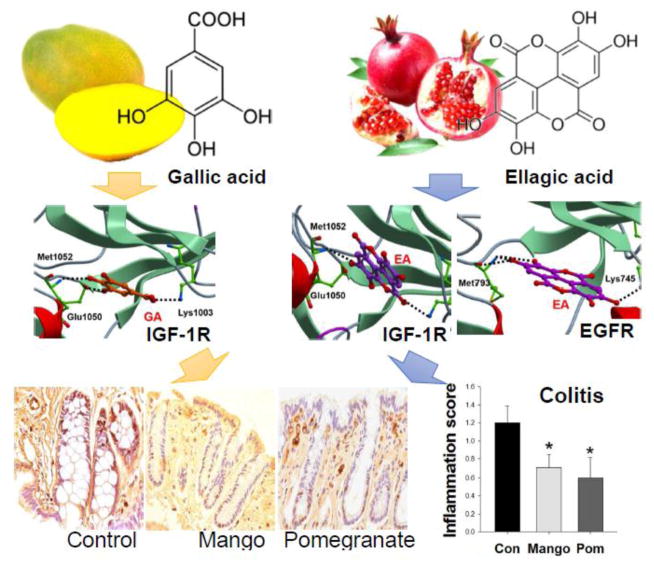
Figure 1. Effects of mango and pomegranate beverages on colonocyte proliferation, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and AKT/mTOR pathway in DSS-treated rats.
Values are the mean ± SEM (n=10 per group). Asterisk indicates significance compared to the control at p<0.05. (A) Experimental design of the in vivo study. (B) Mango and pomegranate beverages decreased the colonocyte proliferative index compared to control beverage in DSS-treated rats (n=10 per group, 25 crypts/rat). (C) There was no difference in the total number of cells on one side of a crypt. (D) Representative images of Ki-67 immunohistochemistry. (E) Mango and pomegranate beverages decreased the expression of hs-CRP and pro-inflammatory cytokines TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 levels in the intestinal mucosa of DSS-treated rats. (F) Mango and pomegranate beverages decreased the levels of IL-1β and IL-6 and increased the level of IL-10 in the DSS-treated rat serum. (G) The phosphorylated/total protein ratios of IR, IGF1R, PTEN, AKT, mTOR, and p70S6K1 were decreased by mango beverage, whereas p70S6K1 and RPS6 ratios were reduced by pomegranate. The dashed bar represents the control group, and the phosphorylation to protein ratio was normalized to the control.