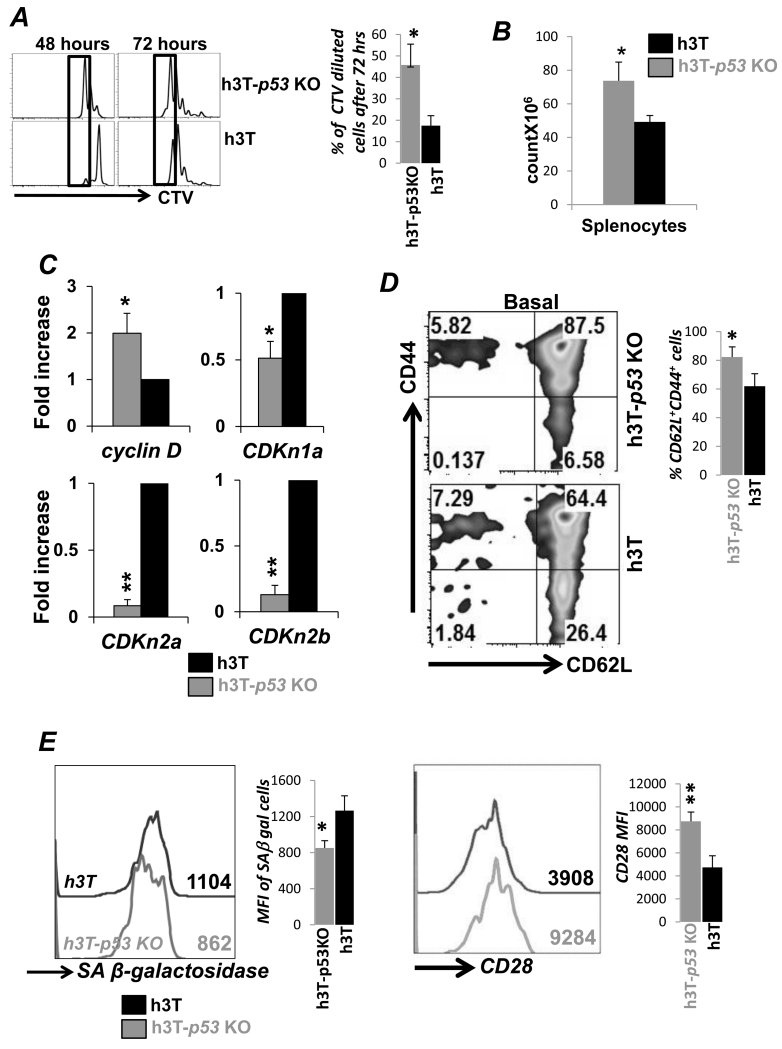
Figure 1. p53 KO T cells preserve Tcm phenotype despite increased proliferation.
A) Splenocytes from the h3T and h3T-p53 KO mouse were harvested and stained with cell trace violet (CTV) dye before stimulating with human tyrosinase peptide pulsed irradiated splenic feeder cells from HLA-A2 mouse. The dilution of CTV dye with time was determined using FACS to evaluate antigen specific proliferation. Adjacent bar diagram shows percent increase in proliferating cells from different experiments. B) Bar diagram representing the total viable splenocytes obtained from three individual h3T and h3T-p53 KO mouse as counted using trypan blue dye. C) Real time quantitative PCR analysis for cyclin D and cyclin inhibitors (CDKn1a, CDKn2a, CDKn2b) was done using RNA obtained from h3T and h3T-p53 KO mouse derived splenic T cells. Data from two repeat experiment is shown. D) Basal cell surface expression of CD44 and CD62L was determined using FACS on Vβ12+ gated splenic T cells from h3T and h3T-p53 KO. Adjacent bar diagram shows percent difference in CD62L+CD44+ T cells from repeat experiments. E) TCR activated splenic T cells from h3T and h3T-p53 KO were used to detrmine expression of senescence associated β-galactosidase as per manufacturer’s protocol, and CD28 expression using FACS. Numerical value represents mean fluorescence intensity. Adjacent bar diagram shows cumulative data from different experiments. (N=3, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).