Figure 3.
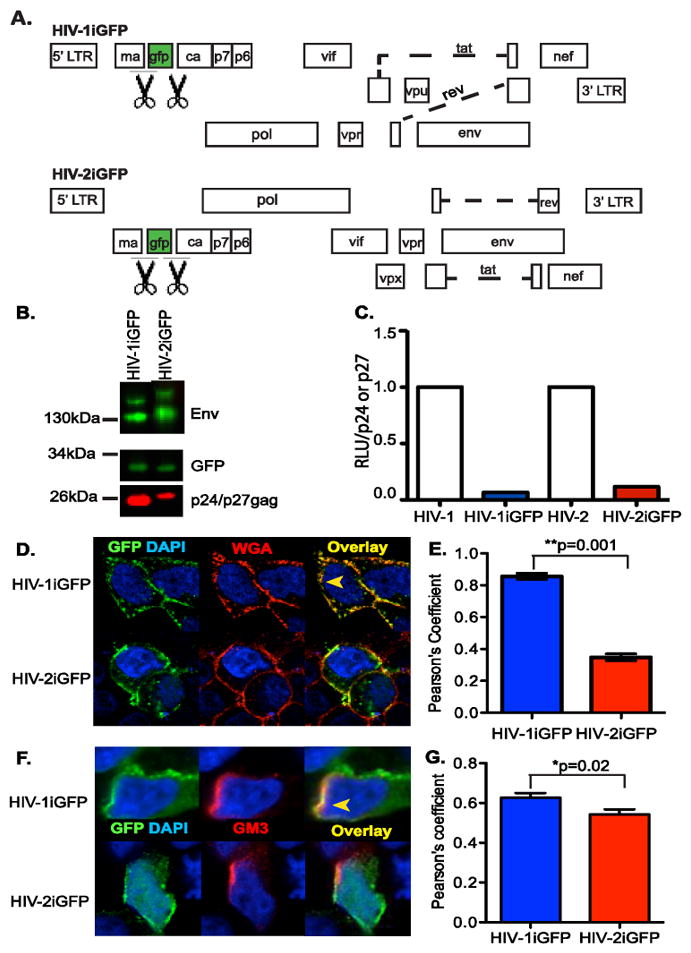
Characterization of HIV-2iGFP. (A) Genome organization of the HIV-1 and HIV-2 proviral plasmids used in this study, which encode GFP between MA and CA, flanked by protease cleavage sites (indicated by the scissors symbol), such that infectious virus particles contain GFP. (B) Representative western blot analysis for Env, GFP, and p24gag or p27gag in virus particle lysates. (C) TZM-bl cells were infected with virus particles (HIV-1/Lai-Bal, HIV-1iGFP, HIV-2/ROD9 or HIV-2iGFP), washed, and cultured for 2 days. Cells were lysed 2 days post infection and the luciferase activity (RLU =relative light units) per p24gag or p27gag measured via TZM-bl infections and AG3.0 ELISA were determined and the values for the iGFP proviruses normalized to that observed with isogenic viruses lacking GFP. The data shown is from a representative experiment (out of 2 independent experiments) performed in triplicate (D) HEK293T cells were transfected with either HIV-1iGFP or HIV-2iGFP plasmid and stained with AlexaFluor 594-conjugated Wheat Germ Agluttinin (WGA-AF594) and counterstained with DAPI, one day post-transfection. (F) HEK293T cells were transfected with either HIV-1iGFP or HIV-2iGFP plasmid and stained with anti-GM3 and AlexaFluor 594-conjugated goat anti-mouse antibodies and counterstained with DAPI, one day post-transfection. The yellow arrowhead in panels D and F indicates an area of co-localization while a white arrowhead indicates lack of co-localization between GFP and WGA (D) or GM3 (F) staining. (E and G) Co-localization between green (GFP) and red (WGA or GM3) is reported as mean (±SEM) Pearson’s coefficient of co-localization. **p=0.001; *p=0.02.
