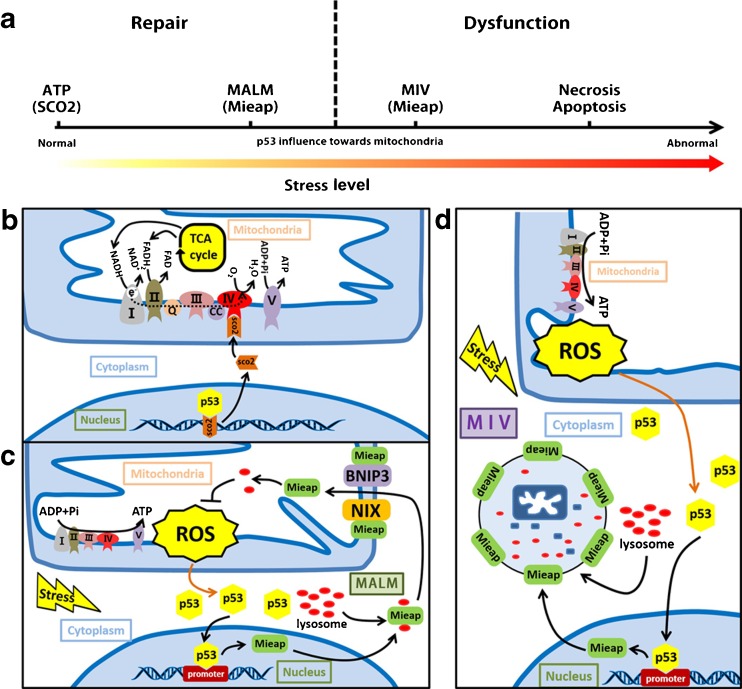
Fig. 1.
p53 plays numerous roles in mitochondria-related processes. a p53 influence towards mitochondria under different stress level. With the enhancement of stress level, mitochondrial function will switch from normal to abnormal in the presence of p53. b p53 regulation and transactivation of mitochondrial Synthesis of Cytochrome c Oxidase 2 (SCO2). The figure shown is the nuclear transactivation of SCO2 by p53. SCO2 is targeted to the inner membrane of the mitochondria where they bind to complex IV and promote aerobic respiratory. When the cell is under the primary stress state, the cells will promote p53 expression keep the balance of the respiration and avoid the Warburg effect and thus, resulting the SCO2 overexpression, but ROS will also be generated during this procedure. c Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosome-like organelles within mitochondria (MALM). Mieap is a p53 inducible protein. Mitochondrial-generated ROS will induce p53 translocation to nuclear and mitochondria. p53 binds to Mieap promoter and leads to the Mieap overexpression. Mieap will binds to NIX and BNIP3, causing the activity change of NIX and BNIP3. These two protein can form a mitochondrial transition-like pore, permitting the translocation of Mieap and lysosome complex into mitochondrial matrix, thus, degenerating ROS and other oxidative protein. d Mieap-induced vacuole (MIV). With the enhancement of stress level, MALM is inhibited, Mieap will form a vacuole and degenerate the impaired mitochondria. Abbreviations: SCO2: mitochondrial Synthesis of Cytochrome c Oxidase 2, MALM: Mieap-induced accumulation of lysosome-like organelles within mitochondria, MIV: Mieap-induced vacuole, ROS: reactive oxygen species, NIX: NIP-like protein X, BNIP3: BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3