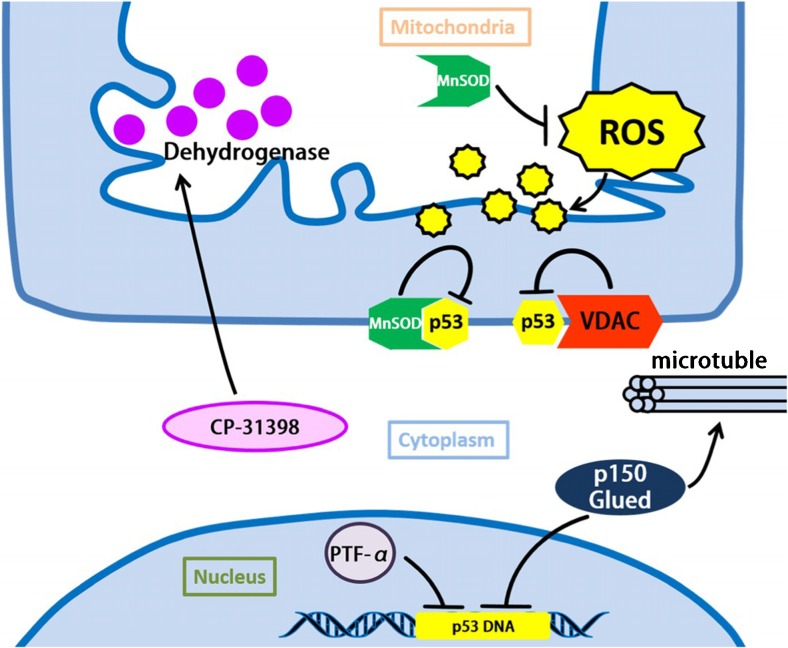
Fig. 6.
Protective molecules and pathways in AD. Mn-SOD contributes as the anti-oxidative factor and is involved in the cellular defense against oxidative damage caused by ROS. Overexpression of MnSOD can inhibit p53 from combining with other protein like Bcl-2. VDAC is found to be connected with restraining p53 under the stress state. CP-31398 is a known compound which can rescue the p53 mutant structure and stabilize the activation of wild-type form. Besides, CP-31,398 can suppress mitochondrial dysfunction by increasing mitochondrial dehydrogenase activity. PFT-α can inhibit p53 transactivation, and result in the suppression of axon degeneration. p150Glued can inhibit p53 transactivation and stabilize microtubule, which modulates mitochondria function and improves axons integrity to avoid excitotoxicity-induced degeneration. Abbreviations: VDAC: voltage-dependent anion channel