Figure 4.
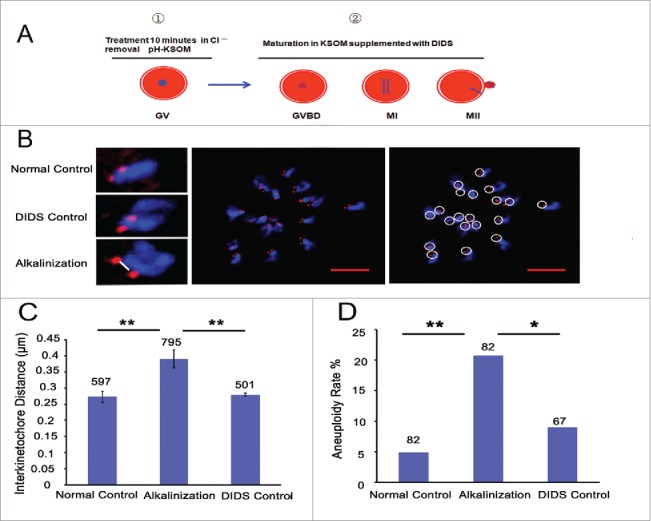
Alkaline treatment of young oocytes causes increases in chromosome aneuploidy and sister iKT distance. (A) Model for the process of alkaline treatment of young oocytes. 1) The pHi of GV oocytes was increased. 2) The increased pHi was maintained in different oocyte phases. (B) MII oocytes were spread in situ. A flattened z-stack series of images through a monastrol-treated egg (middle). Chromosomes were counted using a flattened z-stack series of images; the white circle represents a sister chromatid pair (right). Representative sister chromatid pairs from the normal control, DIDS control and alkaline treatment groups illustrating the increase in iKT distances; the white line shows the inner distance of the sister chromatid pair (left). Red, centromere (CREST); blue, chromatin (4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole, DAPI). Bar = 5 μm. Alkalinization: oocytes were matured in a medium supplemented with DIDS after being removed to Cl−-free media for a 10-min treatment. Normal control: oocytes were matured in media without any addition and treatment. DIDS control: oocytes were matured in media supplemented with DIDS but without Cl−-free media treatment. In C and D, the numbers analyzed are indicated above the bars; ** P < 0.01; * P < 0.05. In each experiment, the data shown represent more than 3 replications.
