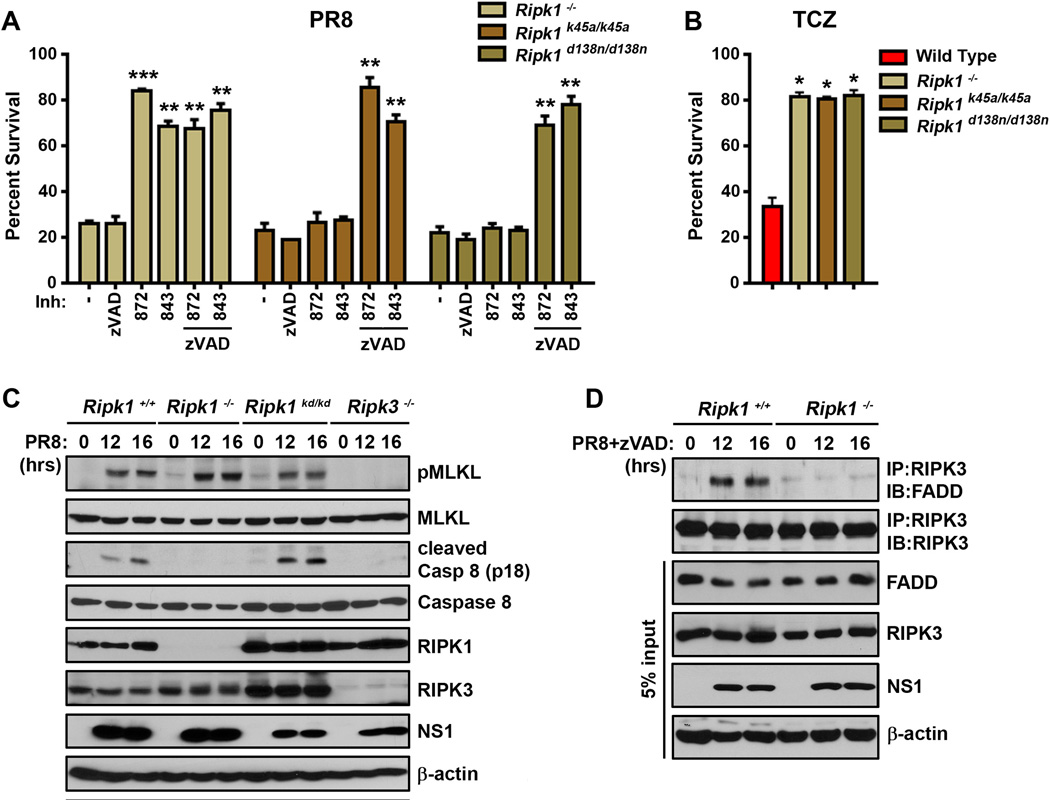
Figure 5. RIPK1 mediates RIPK3-dependent apoptosis in IAV-infected cells.
(A) Ripk1−/−, ripk1k45/a/k45a, and ripk1d138n/d138n MEFs were infected with PR8 (m.o.i.=2) in the presence or absence of zVAD (50µM) or 5µM of the RIPK3 inhibitors GSK’872 or GSK’843, and viability was determined 24 h.p.i. (B) Ripk1−/−, ripk1k45/a/k45a, and ripk1d138n/d138n MEFs were treated with TCZ and viability was determined 24 h.p.i. (C) Ripk1−/−, ripk1d138n/d138n (referred to as ripk1kd/kd), and ripk3−/− MEFs were infected with PR8 and examined for phosphorylated MLKL or cleaved caspase 8 by immunoblot analysis at the indicated times p.i. (D) Ripk1+/+ and ripk1−/− MEFs were infected with PR8 in the presence of zVAD (25µM). Cells were lysed at the indicated time points, and RIPK3-immunoprecipitated lysates were examined for presence of FADD. Error bars represent mean +/− S.D. * p <0.05; ** p <0.005; *** p <0.0005. See also Figs. S2 and S6.